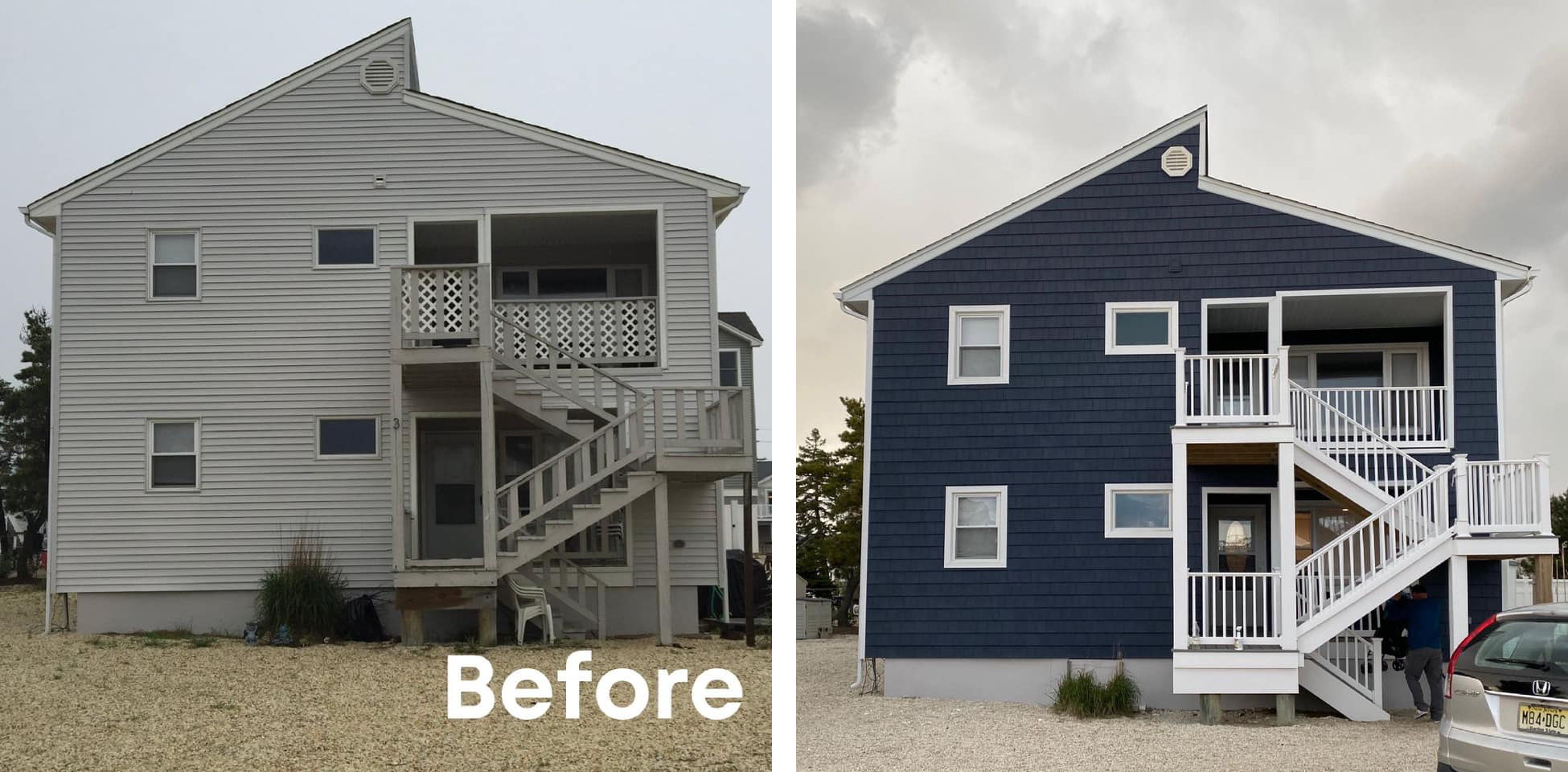
Cost of Replacing Old Aluminum Siding with New Materials is a significant undertaking for homeowners, impacting both aesthetics and long-term value. This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted costs involved, from material selection and labor expenses to permits, waste disposal, and potential unforeseen challenges. We’ll delve into a detailed cost comparison of various siding materials, analyze labor requirements, and illuminate the financial implications of choosing different options. Understanding these costs upfront is crucial for budgeting effectively and making informed decisions about this substantial home improvement project.
This analysis will cover a range of factors impacting the total cost, including material pricing variations (vinyl, fiber cement, wood, etc.), regional labor rates, permit fees, waste disposal methods, and the potential for unexpected repairs. We will also examine the long-term cost implications, considering warranty periods, maintenance requirements, and the potential impact on energy efficiency and home value. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the financial landscape surrounding siding replacement and be better equipped to plan your project.
Material Costs Comparison
Replacing aluminum siding involves a significant investment, and choosing the right material is crucial. This section details the cost differences between various siding options, helping you make an informed decision. We will compare the price per square foot, considering factors that influence the overall expense.
Cost Breakdown of Siding Materials
The cost of siding materials varies significantly depending on the type of material chosen. Aluminum siding, while relatively inexpensive initially, often requires more frequent replacement than other options. Here’s a comparison of material costs per square foot, keeping in mind that these are estimates and can fluctuate based on location, quality, and brand. Prices typically range from a low to high end, accounting for various grades and manufacturers.
| Material | Cost per Square Foot (Low End) | Cost per Square Foot (High End) | Installation Cost per Square Foot (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl Siding | $2.00 | $6.00 | $3.00 – $5.00 |
| Fiber Cement Siding | $4.00 | $12.00 | $5.00 – $8.00 |
| Wood Siding | $6.00 | $20.00+ | $7.00 – $12.00+ |
| Aluminum Siding | $1.50 | $4.00 | $2.00 – $4.00 |
Factors Influencing Material Costs
Several factors contribute to the variation in siding material costs. Understanding these factors will help you better estimate the total cost of your project.
Quality significantly impacts pricing. Higher-quality materials, such as those with enhanced durability, weather resistance, and aesthetic appeal, generally command higher prices. For example, a premium grade of vinyl siding with a longer warranty will cost more than a basic grade. Similarly, fiber cement siding with a thicker profile and enhanced durability will be more expensive than thinner options. Brand recognition also plays a role. Established brands often charge a premium for their reputation and perceived quality.
Regional availability affects pricing. Materials that are readily available in a particular region will generally be less expensive than those that need to be transported long distances. For example, wood siding sourced locally will often be cheaper than wood siding imported from another country. Finally, the current market conditions, including material availability and labor costs, also influence pricing. Economic fluctuations can lead to price increases or decreases in the short term.
Total Estimated Costs
The total estimated cost of siding replacement includes both material and installation costs. Using the data in the table above, we can illustrate the potential total cost for a 1000 square foot home.
| Material | Total Material Cost (1000 sq ft, Low End) | Total Material Cost (1000 sq ft, High End) | Total Installation Cost (1000 sq ft, Estimate) | Total Estimated Cost (Low End) | Total Estimated Cost (High End) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl Siding | $2000 | $6000 | $3000 – $5000 | $5000 – $8000 | $9000 – $11000 |
| Fiber Cement Siding | $4000 | $12000 | $5000 – $8000 | $9000 – $14000 | $17000 – $20000 |
| Wood Siding | $6000 | $20000+ | $7000 – $12000+ | $13000 – $22000+ | $27000 – $32000+ |
| Aluminum Siding | $1500 | $4000 | $2000 – $4000 | $3500 – $6000 | $6000 – $8000 |
Labor Costs Analysis
Labor costs represent a significant portion of the total expense when replacing aluminum siding. Understanding the factors that influence these costs is crucial for accurate budgeting and realistic project planning. Several key variables impact the final labor bill, including the project’s scope, geographical location, and the experience level of the chosen contractor.
Factors Affecting Labor Costs for Siding Replacement
Project Size and Complexity
The size of the house and the complexity of the siding job directly affect the labor hours required. A larger house with intricate architectural details, such as multiple gables, dormers, or bay windows, will naturally demand more time and therefore, higher labor costs than a smaller, simpler structure. For example, a 1,500 square foot ranch-style home will require considerably less labor than a 3,000 square foot Victorian home with numerous architectural features. Additional factors influencing complexity include the need for extensive repairs to underlying sheathing or the presence of obstacles like difficult-to-access areas.
Geographic Location
Labor costs vary significantly across different regions of the country. Areas with a higher cost of living generally have higher labor rates for skilled tradespeople. For instance, contractors in major metropolitan areas like New York City or San Francisco will typically charge more per hour than those in smaller towns or rural areas. This difference reflects the higher demand for skilled labor and the increased operational expenses faced by businesses in these high-cost regions.
Contractor Experience and Expertise
The experience and reputation of the contractor also play a critical role in determining labor costs. Highly experienced and reputable contractors often command higher hourly rates due to their expertise, efficiency, and commitment to quality workmanship. While a less experienced contractor might offer a lower hourly rate, the potential for delays, mistakes, and the need for rework could ultimately increase the overall project cost. Choosing a qualified and experienced contractor may seem more expensive upfront, but it can often save money and stress in the long run.
Labor Hours for Removal and Installation
Removing aluminum siding typically requires more labor than installing new siding materials. Aluminum siding is often fastened securely and can be difficult to remove without damaging the underlying sheathing. Careful removal is essential to avoid unnecessary repairs or replacements. In contrast, installing new siding is generally a more straightforward process, although the specific techniques vary depending on the chosen material (e.g., vinyl, fiber cement, wood). For example, removing aluminum siding on a 2,000 square foot house might take two experienced workers two days, while installing vinyl siding on the same house could take them one and a half days.
Labor Cost Ranges Per Square Foot
The labor cost per square foot for siding replacement varies considerably based on the factors discussed above. However, a general range can be provided as a starting point for budgeting purposes.
| Siding Material | Labor Cost Per Square Foot (USD) |
|---|---|
| Vinyl Siding | $1.50 – $4.00 |
| Fiber Cement Siding | $3.00 – $6.00 |
| Wood Siding | $4.00 – $8.00+ |
Note: These are approximate ranges, and actual costs may vary depending on the specific project details and location. Always obtain multiple detailed quotes from reputable contractors before making a decision.
Permits and Inspections
Replacing your aluminum siding necessitates navigating the often-unfamiliar world of building permits and inspections. These processes, while sometimes perceived as bureaucratic hurdles, are crucial for ensuring your project adheres to local building codes, protects your investment, and safeguards your property’s value. Understanding the associated costs upfront is essential for accurate budgeting.
Permitting and inspection costs for siding replacement projects are highly variable and depend on several key factors. The location of your property significantly influences fees, as each municipality or county establishes its own pricing structure. Project scope also plays a crucial role; a large-scale replacement will naturally incur higher costs than a smaller, localized repair. Additionally, the complexity of the project, including any structural modifications required, can affect the number and type of inspections needed, thus impacting the overall expense.
Permit Fees
Permit fees are typically calculated based on the project’s estimated value. This value is often determined by the cost of materials and labor. For instance, a small siding replacement project might cost $5,000, resulting in a permit fee of around $100 to $300, depending on the local jurisdiction. A larger, more extensive project costing $20,000 might incur a permit fee between $300 and $1000 or even more in some areas. It’s advisable to contact your local building department to obtain precise fee information, which may be available online or in person. Some municipalities offer online permit applications, streamlining the process and providing immediate fee estimates.
Inspection Fees
Inspection fees are usually separate from permit fees and are charged for each inspection required throughout the project. Common inspections include initial plan review, framing inspection (if structural changes are involved), and final inspection once the siding is installed. The number of inspections varies depending on project complexity and local regulations. These fees typically range from $50 to $150 per inspection, potentially adding up to several hundred dollars for a comprehensive siding replacement.
Sample Cost Breakdown for Permits and Inspections
Let’s consider a hypothetical siding replacement project for a single-family home with approximately 1,500 square feet of siding.
| Item | Cost Estimate |
|---|---|
| Permit Application Fee | $200 |
| Plan Review Inspection Fee | $75 |
| Framing Inspection Fee (if applicable) | $100 |
| Final Inspection Fee | $75 |
| Total Estimated Cost for Permits and Inspections | $450 |
This is a sample breakdown, and actual costs may vary considerably depending on the factors discussed earlier. Always obtain specific quotes from your local building department to ensure accurate budgeting. It’s also prudent to factor in potential delays related to permitting and inspections; unforeseen issues may require additional inspections or amended applications, potentially increasing costs and extending the project timeline.
Waste Removal and Disposal
Replacing your aluminum siding generates significant waste, and responsible disposal is crucial both environmentally and financially. The cost of waste removal and disposal can vary considerably depending on factors such as the volume of waste, the type of materials, local regulations, and the chosen disposal method. Understanding these costs is essential for accurate budgeting.
Proper disposal of old aluminum siding and construction debris is not only environmentally responsible but also often legally mandated. Failing to comply with local regulations can result in significant fines. Moreover, choosing environmentally friendly options can reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future. The following sections detail various disposal methods and their associated costs.
Costs Associated with Waste Disposal
The cost of disposing of old aluminum siding and construction debris depends on several factors. The volume of waste is a primary driver of cost; larger projects naturally generate more waste and require more extensive removal services. The type of waste also plays a role; aluminum siding, while recyclable, may require specialized handling compared to regular construction debris like wood or drywall. Local regulations concerning waste disposal significantly influence costs, with some areas having stricter rules and higher fees than others. Finally, the chosen disposal method, whether it involves a dumpster rental, specialized hauling services, or recycling programs, directly impacts the overall expense. For example, a small residential project might cost between $200 and $500 for waste removal, while a larger commercial project could easily exceed $1000 or more.
Environmentally Friendly Disposal Options
Recycling is a key component of environmentally responsible waste disposal. Aluminum siding, being a highly recyclable material, can be processed and reused, minimizing landfill waste. Many recycling centers accept aluminum siding, often at a cost lower than simply disposing of it in a landfill. However, the cost of transportation to the recycling center should be considered. Another environmentally conscious approach involves utilizing construction debris for fill material on the property, if feasible and permitted. This reduces the amount of waste that needs to be transported off-site, thus minimizing transportation costs and carbon emissions. This option is contingent upon the project scale and local regulations. Composting of organic waste generated during the project, such as wood scraps, is another sustainable practice that reduces landfill waste.
Waste Removal and Disposal Methods and Costs
The following list outlines common waste removal and disposal methods and their associated cost implications. Costs are estimates and can vary widely depending on location and project specifics.
- Dumpster Rental: This is a common method for disposing of large volumes of construction debris. Costs range from $300 to $800 or more, depending on the dumpster size and rental duration. This often includes delivery and pickup.
- Specialized Hauling Services: For projects with specific waste disposal needs, such as hazardous materials or large quantities of aluminum siding, specialized hauling services are often necessary. These services typically charge by the weight or volume of waste, resulting in costs that can vary significantly. Expect to pay a premium for this service compared to dumpster rentals.
- Recycling Centers: Recycling aluminum siding can significantly reduce disposal costs compared to landfill disposal. Costs vary depending on the recycling center’s fees and the amount of aluminum being recycled. Some centers may even pay for the recyclable aluminum.
- On-site Material Reuse: If appropriate and permitted, reusing construction debris (like wood or broken pieces of siding for backfill) as fill material can significantly reduce waste disposal costs, potentially eliminating the need for other methods altogether.
Unexpected Expenses
Replacing your aluminum siding is a significant undertaking, and while careful planning can minimize costs, unforeseen expenses are a common reality. These unexpected costs can significantly impact your budget, so it’s crucial to be prepared for potential surprises. Understanding the potential causes and ranges of these expenses will help you better manage your project’s finances.
Unexpected expenses often stem from issues discovered only after the old siding is removed. This reveals the underlying structure of your home, exposing problems that may have been hidden for years. For example, extensive water damage might necessitate more extensive repairs than initially anticipated, increasing both material and labor costs. Similarly, structural problems like damaged sheathing or framing may require significant repairs before new siding can be installed. The age and condition of your home play a crucial role in determining the likelihood and extent of these unexpected costs.
Unforeseen Structural Issues
Discovering unforeseen structural problems during siding removal is a common cause of budget overruns. These problems could include rotted wood sheathing, damaged framing, or insect infestation. The extent of the damage dictates the necessary repairs, ranging from simple patching to extensive replacement of sections of the wall. For instance, finding significant water damage behind a section of siding might necessitate replacing multiple boards of sheathing, adding several hundred dollars to the project cost, depending on the extent of the damage and the cost of materials and labor in your area. In severe cases, it could even involve structural reinforcement, substantially increasing the total cost.
Hidden Water Damage
Water damage, often hidden beneath the old siding, can be a significant source of unexpected expenses. Mold growth, rotted wood, and damaged insulation are all possibilities. The cost to repair water damage can vary widely, depending on the severity and location of the problem. A small area of water damage might cost a few hundred dollars to repair, while extensive damage could cost thousands. For example, water damage requiring the replacement of a large section of wall sheathing, along with insulation and vapor barrier, could easily add $1,000 – $3,000 or more to the overall project cost.
Unexpected Material Needs
The initial material estimate may not fully account for all necessary supplies. This can happen due to unforeseen issues like discovering damaged areas requiring more materials than anticipated or needing specialized materials for unexpected repairs. For instance, discovering rotted wood behind the siding might necessitate purchasing additional lumber and treatments for proper repair, adding to the initial material cost. Also, if specialized flashing or sealant is required for unexpected conditions, this can add an unexpected cost to the budget.
Additional Labor Costs
Unforeseen complications can significantly increase labor costs. Discovering extensive damage, requiring more time and effort for repairs, is a frequent cause. For instance, if unexpected structural issues require extensive repairs, the labor costs can increase substantially as more time is needed for demolition, repair, and installation. This could add hundreds or even thousands of dollars to the original labor estimate. Similarly, dealing with unexpected obstacles, such as difficult-to-access areas or complex configurations, will also drive up labor costs.
Potential Unexpected Costs and Their Ranges
It is important to note that these are estimates and actual costs can vary widely depending on location, the extent of the damage, and the contractor’s rates.
| Unexpected Expense | Likely Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Repairing rotted sheathing | $200 – $2,000+ |
| Repairing water damage | $100 – $3,000+ |
| Addressing insect infestation | $300 – $1,500+ |
| Unforeseen structural repairs | $500 – $5,000+ |
| Additional material costs | $100 – $1,000+ |
| Increased labor costs | $200 – $2,000+ |
Warranty and Maintenance Costs
Choosing new siding involves a significant investment, and understanding the long-term costs associated with warranties and maintenance is crucial for making an informed decision. Different siding materials offer varying warranty periods and require different levels of upkeep, directly impacting your overall expenses over the lifespan of your home’s exterior. This section compares the warranty coverage and maintenance requirements of several popular siding options to help you assess the total cost of ownership.
Warranty Periods for Different Siding Materials
Warranty periods vary considerably depending on the manufacturer, material type, and specific product. For example, vinyl siding often comes with a 20-30 year warranty against manufacturing defects, while fiber cement siding may offer a 50-year warranty, though this often excludes certain aspects like paint finish. Aluminum siding warranties are typically shorter, ranging from 15-25 years. The length of the warranty doesn’t necessarily reflect the material’s lifespan; it primarily covers defects in manufacturing and materials. It’s crucial to carefully review the specific terms and conditions of each warranty before making a purchase.
Maintenance Requirements and Associated Costs
The maintenance needs of different siding materials vary significantly, impacting long-term costs. Vinyl siding is generally low-maintenance, requiring only occasional cleaning with soap and water. However, more extensive cleaning might be needed to remove stubborn stains or mildew. Fiber cement siding requires more attention; it may need periodic repainting to maintain its appearance and protect it from the elements. Aluminum siding, while durable, can be susceptible to dents and scratches, potentially requiring repairs or replacement of individual panels. Regular inspection for damage and prompt repairs are key to minimizing long-term expenses.
Long-Term Cost Implications
Considering maintenance and potential repairs over a 20-year period provides a clearer picture of the overall cost of each siding option. For example, while vinyl siding may have lower initial costs, frequent repainting of fiber cement siding over two decades might offset this initial savings. Aluminum siding’s potential for damage and the need for individual panel replacements could also lead to considerable costs over the long term. Unforeseen events, such as severe weather damage, could necessitate repairs or replacements irrespective of the material choice. Proper planning and budgeting for these eventualities are essential.
Warranty and Maintenance Cost Comparison (20-Year Period)
| Siding Material | Warranty Period (Years) | Estimated Annual Maintenance Cost | Estimated Total Maintenance Cost (20 Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | 25-30 | $50 | $1000 – $1200 |
| Fiber Cement | 50 (material, paint separate) | $150 – $200 (includes repainting every 7-10 years) | $3000 – $4000 |
| Aluminum | 15-25 | $75 – $100 (includes potential minor repairs) | $1500 – $2000 |
*Note: These are estimated costs and can vary based on factors such as home size, climate, and specific product choices. Actual costs may be higher or lower.
Financing Options
Replacing your home’s siding is a significant investment, and securing appropriate financing can make the project more manageable. Several options exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages concerning interest rates and repayment terms. Choosing the right financing method depends on your financial situation and the overall cost of your project.
Financing a siding replacement project typically involves either loans specifically designed for home improvements or using existing credit lines like credit cards. Home improvement loans often offer lower interest rates than credit cards, making them a more cost-effective choice for larger projects. However, credit cards can provide quicker access to funds, which might be beneficial if you need to start the project immediately.
Home Improvement Loans
Home improvement loans are specifically designed to finance projects like siding replacement. These loans typically offer fixed interest rates and repayment terms ranging from several months to several years. The interest rate offered will depend on several factors, including your credit score, the loan amount, and the lender. Lenders often require a down payment, and the loan amount is usually capped at a certain percentage of your home’s value.
Credit Card Financing
Using a credit card to finance a siding replacement project offers immediate access to funds. However, credit cards typically carry higher interest rates than home improvement loans, making them more expensive in the long run. Interest charges can quickly accumulate if the balance isn’t paid off promptly. It’s crucial to understand the APR (Annual Percentage Rate) and any associated fees before using a credit card for such a significant expense.
Examples of Financed Siding Replacement Costs
Let’s consider a hypothetical siding replacement project costing $15,000. Below are examples illustrating the total cost when financed with different loan terms and interest rates. These are simplified examples and do not include any potential closing costs or fees. Actual costs will vary based on lender specifics and individual circumstances.
| Loan Type | Loan Amount | Interest Rate | Loan Term (Years) | Approximate Monthly Payment | Total Cost (Principal + Interest) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Home Improvement Loan | $15,000 | 6% | 5 | $286.97 | $17,218.20 |
| Home Improvement Loan | $15,000 | 8% | 5 | $299.78 | $17,986.80 |
| Credit Card | $15,000 | 18% | 5 | $373.96 | $22,437.60 |
Note: These are estimates only. Actual payments and total costs may vary depending on the lender and specific loan terms. Always compare offers from multiple lenders before making a decision.
Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Replacing your old aluminum siding presents a valuable opportunity to enhance your home’s energy efficiency. The choice of siding material significantly impacts your home’s insulation properties, directly affecting heating and cooling costs. By carefully considering the thermal resistance (R-value) of different materials, you can make an informed decision that leads to long-term cost savings.
Improved insulation reduces the amount of energy needed to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. This translates to lower energy bills and a smaller carbon footprint. The initial investment in new siding with superior insulation can be offset by these savings over the lifespan of the material. The payback period, or the time it takes for the energy savings to equal the initial investment, varies depending on factors such as energy prices, climate, and the R-value of the chosen siding.
Comparison of Siding Material Insulation Properties
Different siding materials offer varying levels of insulation. For example, vinyl siding typically boasts an R-value between 0.5 and 1.0, while fiber cement siding ranges from 0.1 to 0.3. Wood siding, depending on its thickness and type, can offer R-values from 0.8 to 1.3. However, the overall insulation of the wall system is a combination of the siding and the underlying insulation, making the siding’s contribution relative. The most effective approach involves maximizing the insulation within the wall cavity, regardless of the exterior siding material. This means focusing on proper installation of appropriate insulation batt thickness for your climate zone.
Energy Savings Calculation: A Hypothetical Example
Let’s consider a hypothetical example to illustrate the potential energy savings. Assume a 2,000 square foot home in a climate with average annual heating and cooling costs of $2,000. Replacing the aluminum siding (with negligible insulation value) with vinyl siding (R-value of 0.8) might reduce energy consumption by 5%, leading to annual savings of $100 ($2000 x 0.05). However, if the same home uses fiber cement siding (R-value of 0.2) and also improves the wall insulation with additional batt insulation (e.g., from R-13 to R-21), the energy savings could be significantly higher, perhaps reaching 15% or $300 annually. These savings accumulate over time, potentially offsetting the higher initial cost of the siding and insulation upgrade. It’s crucial to note that actual savings will vary based on numerous factors, including the home’s construction, climate, and energy usage patterns. A detailed energy audit can provide a more accurate prediction of potential savings.
Offsetting Initial Costs Through Energy Savings
The initial cost of replacing siding, including labor and materials, can be substantial. However, the cumulative energy savings realized over the lifespan of the new siding can significantly offset this expense. For instance, if the energy savings from a siding upgrade amount to $300 annually and the siding is expected to last 30 years, the total savings would be $9000. This figure could easily surpass the initial cost of the project, resulting in a net positive return on investment. This makes energy efficiency a critical consideration when planning a siding replacement project. A simple payback calculation can help determine if the long-term savings justify the upfront investment.
Home Value Impact
Replacing your home’s siding can significantly impact its overall value, often providing a substantial return on investment. The choice of material plays a crucial role in determining how much this impact will be, influencing both the perceived aesthetic appeal and the perceived durability of the home. A well-chosen siding upgrade can enhance curb appeal and attract potential buyers, leading to a higher selling price.
The choice of siding material directly influences the perceived value of a home. Higher-end materials, such as fiber cement or engineered wood, tend to command a greater premium than vinyl or aluminum siding. This is because these materials are often associated with increased durability, longevity, and a more upscale aesthetic. Conversely, while vinyl siding can be an affordable option, it may not add as much value to a home as more premium materials.
Siding Material and Resale Value
Different siding materials affect the potential resale value of a property in varying ways. For instance, a home with newly installed fiber cement siding, known for its durability and fire resistance, might see a larger increase in value compared to a home with newly installed vinyl siding. This is because fiber cement is perceived as a higher-quality, more long-lasting material. Similarly, a home featuring cedar or other natural wood siding, if properly maintained, can significantly enhance its perceived value due to its aesthetic appeal and association with luxury. However, the increased maintenance required for natural wood siding should be considered. Conversely, aluminum siding, while durable, might not increase the home’s value as dramatically as other materials due to its more common and less-expensive nature.
Examples of Resale Value Impact
Consider a hypothetical scenario: Two identical homes in the same neighborhood are listed for sale. One home features original aluminum siding showing signs of age and wear, while the other has recently been sided with high-quality fiber cement. The home with the upgraded fiber cement siding is likely to command a higher price and sell faster due to its improved curb appeal and the perceived increase in quality and longevity. Another example could involve a home with older vinyl siding replaced with cedar shake siding. The cedar shake, while more expensive initially, might significantly increase the home’s value due to the upscale appearance and the inherent appeal of natural materials, assuming proper maintenance. The final sale price difference between these comparable homes could easily reach several thousand dollars, reflecting the impact of siding choice on resale value. These examples demonstrate the financial benefits of investing in higher-quality siding materials, even though the initial cost may be higher.
Ultimate Conclusion
Replacing old aluminum siding offers a fantastic opportunity to enhance your home’s curb appeal, improve energy efficiency, and potentially increase its value. However, navigating the associated costs requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the financial aspects, from material costs and labor expenses to permits, waste disposal, and potential unforeseen expenses. By understanding the potential cost ranges for different materials and factoring in long-term implications, homeowners can make informed decisions that align with their budget and long-term goals. Remember to obtain multiple quotes from reputable contractors to ensure you’re getting the best value for your investment.