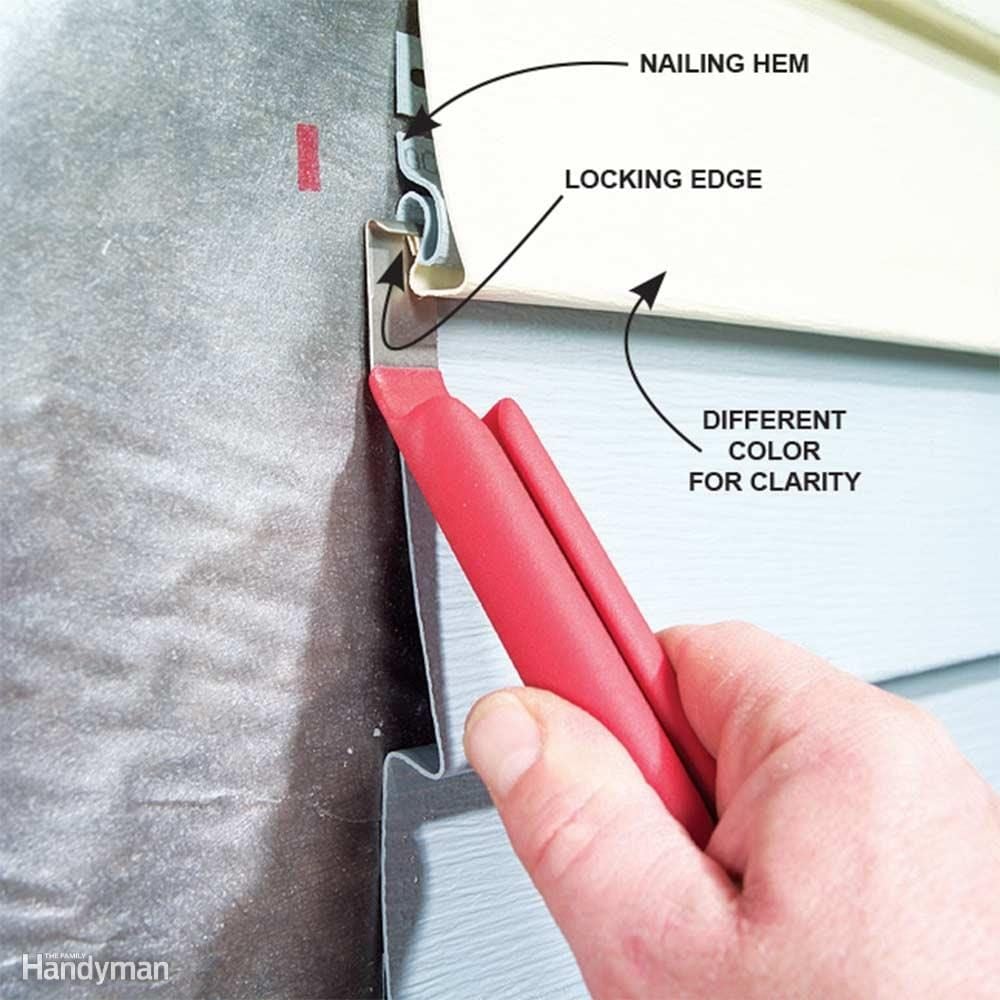
Best Tools for DIY Vinyl Siding Installation: Transforming your home’s exterior with new vinyl siding is a rewarding project, but success hinges on having the right tools. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of essential tools, from measuring and cutting instruments to fastening devices and safety equipment, ensuring a smooth and efficient installation. We’ll explore premium options, highlight key features, and emphasize the importance of quality tools for a professional-looking finish that enhances your home’s curb appeal and value.
This detailed exploration covers everything from selecting the appropriate vinyl siding type and preparing your home’s surface to mastering precise cutting techniques and navigating tricky areas like corners and windows. We’ll also guide you through the installation process, emphasizing safety precautions and troubleshooting common problems. With our step-by-step instructions, budgeting tips, and a comprehensive FAQ section, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle this DIY project with confidence.
Essential Tools for Vinyl Siding Installation
Successful vinyl siding installation hinges on using the right tools. The proper tools ensure efficient work, a professional finish, and minimize the risk of damage to the siding itself. Investing in high-quality tools, while initially more expensive, ultimately saves time and money by preventing costly mistakes and ensuring a long-lasting installation.
Essential Tools Categorized by Function
Choosing the right tools is paramount for a smooth and efficient vinyl siding installation. The following table categorizes essential tools based on their function, highlighting brand recommendations and key features. Remember that the specific needs may vary slightly depending on the project’s size and complexity.
| Tool Name | Tool Type | Purpose | Brand Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Measuring Tape | Measuring | Accurate measurement of walls and siding panels for cutting and placement. A long tape measure (at least 25 feet) is essential for large projects. | Stanley, Lufkin |
| Chalk Line | Measuring/Marking | Creates straight lines for accurate siding alignment, ensuring a neat and professional look. | Johnson Level & Tool, Empire |
| Circular Saw with Fine-Tooth Blade | Cutting | Precisely cuts vinyl siding panels to size. A fine-tooth blade minimizes chipping and ensures clean cuts. | DeWalt, Makita |
| Jigsaw | Cutting | Useful for intricate cuts around windows, doors, and corners where a circular saw may be difficult to maneuver. | Bosch, Ryobi |
| Utility Knife | Cutting | Used for trimming and smaller cuts. A sharp blade is crucial for clean cuts. | Olfa, Stanley |
| Tin Snips | Cutting | Specifically designed for cutting metal, useful for cutting flashing and other metal components around windows and doors. | Malco, Wiss |
| Power Drill with Drill Bits | Fastening | Drills pilot holes for screws and nails, ensuring the siding is securely fastened without splitting. | DeWalt, Milwaukee |
| Impact Driver | Fastening | Provides powerful torque for driving screws quickly and efficiently, especially useful with longer screws. | Milwaukee, Makita |
| Nail Gun (Optional, but Recommended for Larger Projects) | Fastening | Significantly speeds up the fastening process, especially for larger projects. Requires proper safety precautions. | Senco, Hitachi |
| Level | Alignment | Ensures the siding is installed level and plumb, crucial for a professional and aesthetically pleasing finish. | Johnson Level & Tool, Stabila |
| Safety Glasses | Safety | Protects eyes from flying debris during cutting and fastening. | 3M, DEWALT |
| Work Gloves | Safety | Protects hands from cuts and splinters. | Carhartt, Mechanix Wear |
| Ladder | Accessibility | Provides safe access to higher areas during installation. Ensure it is appropriately sized and stable. | Werner, Little Giant |
| Caulk Gun | Finishing | Applies caulk to seal gaps and joints, preventing water infiltration. | DeWalt, DAP |
| Putty Knife | Finishing | Used for smoothing caulk and removing excess material. | Marshalltown, Goldblatt |
Importance of High-Quality Tools
Using high-quality tools is not merely a matter of preference; it directly impacts the final outcome. Premium tools, such as those from brands like DeWalt and Milwaukee, offer superior durability, precision, and ease of use. This translates to cleaner cuts, faster installation times, and a more professional-looking finished product. Investing in robust tools reduces the likelihood of tool failure mid-project, saving both time and frustration. Furthermore, the precision offered by high-quality tools minimizes the risk of damaging the vinyl siding, a costly mistake to rectify.
Choosing the Right Vinyl Siding
Selecting the appropriate vinyl siding is crucial for a successful DIY installation and a long-lasting, aesthetically pleasing exterior. The choice involves considering several factors beyond just the initial cost, encompassing durability, visual appeal, and the overall style of your home. Making informed decisions in these areas will ensure a satisfying outcome.
Choosing the right vinyl siding involves careful consideration of various factors, including the type of siding, its color and texture, and the manufacturer’s warranty. Understanding these aspects will lead to a successful project that enhances your home’s curb appeal and protects it for years to come.
Vinyl Siding Types: A Comparison
Different types of vinyl siding offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. The three most common types—clapboard, shingle, and shake—each provide unique aesthetic qualities and levels of durability. Careful consideration of these factors will help you select the best option for your home.
- Clapboard: This classic style mimics traditional wood clapboard siding. It’s known for its clean lines and versatile appearance, suitable for a wide range of architectural styles. Clapboard siding generally offers good durability and is relatively easy to install. Cost is typically moderate.
- Shingle: Shingle siding offers a more textured and dimensional look, often resembling wood or slate shingles. It can add visual interest and depth to a home’s exterior. Durability is generally good, though some shingle styles might be more susceptible to damage from high winds. Cost can vary depending on the complexity of the shingle design.
- Shake: Shake siding replicates the look of wood shakes, providing a rustic and natural appearance. It offers a more rugged texture than clapboard or shingle. Durability can be slightly lower than clapboard due to the increased surface area, making it potentially more susceptible to wind damage. The cost is typically higher than clapboard but can be comparable to more intricate shingle designs.
Siding Color and Texture Selection
The color and texture of your vinyl siding significantly impact your home’s overall aesthetic. Harmonizing these elements with your home’s architectural style and surrounding landscape is essential for a cohesive and visually appealing result.
Consider the following factors when choosing siding color and texture:
* House Style: A traditional home might benefit from classic clapboard in a neutral color, while a modern home might suit sleek, textured panels in a bold color.
* Surrounding Environment: Consider the colors of your landscaping, neighboring homes, and the overall tone of your neighborhood. A color that clashes with its surroundings will detract from the home’s overall appeal.
* Light Exposure: Darker colors absorb more heat, potentially increasing energy costs in warmer climates. Lighter colors reflect sunlight and can help keep the home cooler. The direction your house faces also impacts the amount of sun exposure.
* Personal Preference: Ultimately, the best color and texture are those that you find aesthetically pleasing.
Manufacturer Warranties and Certifications
Checking for manufacturer warranties and certifications is paramount before purchasing vinyl siding. These assurances provide peace of mind and protect your investment.
Reputable manufacturers offer warranties covering defects in materials and workmanship. Look for warranties that cover a substantial period, typically 20-30 years or more. Certifications, such as those from organizations like the Vinyl Siding Institute (VSI), indicate that the product meets specific quality standards. These certifications ensure the siding is manufactured to high standards and will perform as expected. Choosing products with such warranties and certifications minimizes the risk of premature failure and provides recourse if problems arise.
Preparing the Surface for Installation
Proper surface preparation is paramount for a successful and long-lasting vinyl siding installation. A well-prepared surface ensures the siding adheres correctly, preventing issues like warping, buckling, or premature failure. Neglecting this crucial step can lead to costly repairs and significantly shorten the lifespan of your new siding. This section details the necessary steps to prepare your existing wall surface.
Addressing existing wall problems before installing vinyl siding is essential for a successful project. Ignoring these issues can lead to problems down the road, compromising the longevity and aesthetics of your new siding. Careful inspection and remediation will ensure a smooth and trouble-free installation.
Surface Preparation Steps
The following steps outline the process of preparing your wall for vinyl siding installation. Each step plays a vital role in achieving a high-quality, durable finish.
- Cleaning the Surface: Thoroughly clean the existing wall surface to remove dirt, loose paint, cobwebs, and any other debris. Power washing is often effective but use caution to avoid damaging the underlying structure. For stubborn stains, consider using a suitable cleaning solution appropriate for the existing wall material (e.g., wood, brick, concrete). Allow the surface to completely dry before proceeding.
- Repairing Damage: Inspect the wall for any damage, such as cracks, holes, loose mortar (in brick or masonry walls), or rotting wood. Repair all damage using appropriate materials. For instance, cracks in wood can be filled with wood filler, while holes can be patched with cement or specialized repair compounds. Ensure repairs are level with the surrounding surface and allowed to fully cure before further steps.
- Addressing Moisture Issues: Check for signs of moisture penetration, such as water stains, mold, or mildew. Address any moisture problems before installing siding. This might involve repairing damaged flashing, sealing cracks, or addressing underlying water intrusion issues. In cases of significant water damage, professional assistance might be required.
- Removing Obstructions: Remove any obstructions from the wall, such as old siding, loose trim, or protruding nails. Carefully remove any loose or damaged materials to ensure a clean and level surface for the new siding. Ensure all nails and fasteners are removed to prevent damage to the new siding during installation.
Identifying and Addressing Common Wall Surface Problems
Various wall surface problems can negatively impact vinyl siding installation. Recognizing and correctly addressing these issues is critical for a successful outcome. Ignoring these issues can lead to problems with adhesion, warping, and premature failure of the siding.
- Loose or Rotting Wood: Replace any rotten or damaged wood immediately. Failure to do so will lead to the decay spreading behind the new siding, causing significant problems.
- Cracked or Damaged Stucco: Repair any cracks or damaged areas of stucco using a suitable patching compound. Ensure the repair is smooth and level with the surrounding surface.
- Uneven Surfaces: Uneven surfaces can lead to gaps and inconsistencies in the siding installation. Use shims or other leveling techniques to create a smooth, consistent surface before installation.
- Insect Infestation: Address any evidence of insect infestation before proceeding with the installation. This might involve treatment with insecticides or other pest control measures. Allow sufficient time for treatment to be effective before starting the siding installation.
Measuring and Cutting Vinyl Siding Panels
Precise measurement and cutting are crucial for a professional-looking vinyl siding installation. Inaccurate cuts lead to gaps, misaligned panels, and an overall unprofessional appearance. This section details the process of accurately measuring and cutting vinyl siding panels to ensure a seamless and aesthetically pleasing finish.
Accurate measurement begins with careful planning. Before cutting any panels, thoroughly measure each wall section, noting any obstructions like windows, doors, and corners. Remember to account for overlaps and expansion gaps. Always measure twice and cut once to minimize waste and ensure a perfect fit. Use a tape measure that’s long enough to span the entire length of the panels you’ll be cutting. A metal tape measure is preferred for its durability and accuracy.
Cutting Vinyl Siding Panels
Vinyl siding is relatively easy to cut, but precision is key. The most common tools used for cutting are a sharp utility knife, a circular saw with a fine-tooth blade, or a miter saw. A utility knife is ideal for shorter cuts and intricate details, while a circular or miter saw is better for longer, straighter cuts. Regardless of the tool used, always support the panel firmly to prevent chipping or bending.
Use a sharp blade to ensure a clean cut. A dull blade can cause the vinyl to tear or chip, resulting in an uneven finish.
When using a circular saw, ensure the blade is set to the correct depth to avoid cutting through the entire panel. A miter saw is particularly useful for making precise angle cuts, especially for corners and mitered joints. Remember to always wear appropriate safety gear, including safety glasses and gloves, when using power tools.
Handling Tricky Areas: Corners, Windows, and Doors
Corners, windows, and doors require special attention. For exterior corners, use J-channels or corner posts to create a clean, finished look. Measure carefully to ensure the siding fits snugly against the corner post. Around windows and doors, use appropriate trim pieces, such as window and door starter strips, to ensure a professional and weathertight seal.
For inside corners, carefully measure and cut the siding panels to fit snugly, ensuring a tight seal. Use a caulking gun to seal any gaps for added weather protection.
When cutting around windows and doors, it’s crucial to measure the openings precisely. Use a pencil to mark the cut lines directly onto the vinyl siding, ensuring accurate placement of the trim. Remember to account for expansion and contraction of the siding due to temperature changes, leaving appropriate gaps. Always pre-drill pilot holes before driving screws into the siding to prevent splitting. This is especially important when working with harder vinyl types.
Installing Vinyl Siding Panels
Installing vinyl siding panels is the culmination of your preparation and planning. This process requires careful attention to detail to ensure a professional-looking and weather-resistant finish. Remember to always consult the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific siding product, as techniques may vary slightly.
Starting the Installation
Begin installation at the bottom of the wall, starting with a starter strip. This strip provides a level base for the subsequent panels and ensures a straight, even line across the entire installation. It is typically installed horizontally along the foundation or bottom trim. Ensure it is perfectly level and securely fastened using appropriate fasteners. The starter strip will create a clean bottom edge to your siding and hide the lower edge of the first panel.
Installing Subsequent Panels
Once the starter strip is in place, begin installing the first course of siding panels. Slide the bottom edge of the panel into the starter strip, ensuring a tight fit. Each panel should overlap the previous one, with the top edge of the lower panel slightly overlapping the bottom edge of the upper panel. This overlap creates a weather-tight seal and adds to the strength of the siding system. Fasten each panel using appropriate nails or screws, typically near the top and bottom edges of the panel, avoiding the locking mechanism to prevent damage. The fasteners should be driven in straight and firmly, but not so tightly that they distort the panel. Avoid overdriving the fasteners, as this could lead to cracking or damage to the vinyl siding.
Panel Overlap and Alignment
Maintaining consistent overlap and alignment is crucial for a professional finish. Each panel should overlap the previous one by the manufacturer’s specified amount, usually about an inch. This ensures a watertight seal and prevents water penetration behind the siding. Regularly check the alignment of the panels using a level to ensure vertical and horizontal straightness. Use a measuring tape to verify consistent panel spacing and overlap. Minor adjustments can be made by carefully sliding the panels into place. Significant misalignment may require removing and reinstalling the panel.
Fastening Techniques
Vinyl siding should be fastened securely but gently. Use galvanized nails or screws specifically designed for vinyl siding. Avoid using standard nails, as they can damage the vinyl. Drive the fasteners in at an angle slightly away from the panel’s locking mechanism, usually about a quarter of an inch from the edge. This prevents the panel from being damaged by the fastener and allows for expansion and contraction of the vinyl due to temperature changes. The fasteners should be just snug, allowing for slight movement. Over-tightening can cause warping or cracking of the panels.
Working Upwards and Finishing
Continue installing panels in horizontal courses, working your way upwards. Always maintain consistent overlap and alignment. Pay close attention to corners and windows, using appropriate J-channels, corner posts, and trim pieces to create a neat and finished look. These accessories are essential for a professional-looking installation. As you approach the top of the wall, use appropriate finishing pieces to complete the installation and provide a neat and weather-resistant top edge. Remember to always consult the manufacturer’s instructions for specific details on finishing and trim pieces.
Working with J-Channels, Corners, and Trim
Proper installation of J-channels, corners, and trim pieces is crucial for achieving a professional and weathertight vinyl siding installation. These components not only provide a finished look but also protect the underlying structure from moisture and damage. Careful attention to alignment, sealing, and accurate cutting is essential for a successful outcome.
J-Channel Installation
J-channels are used to create a clean, finished edge at the start and end of siding rows, around windows and doors, and at other transitions. Begin by ensuring the J-channel is properly aligned and plumb. Use a level to check its verticality and make any necessary adjustments. Secure the J-channel to the framing using appropriate fasteners, ensuring they are spaced evenly and don’t penetrate the channel too deeply. Apply a bead of high-quality exterior-grade sealant along the top edge of the J-channel before installing the siding to create a weatherproof seal. This prevents water from penetrating behind the siding. Overlap the J-channel slightly at corners to ensure a continuous seal.
Corner Installation
Vinyl siding corners provide a neat and finished look at exterior corners. Similar to J-channels, corners should be plumb and aligned before fastening. Start by positioning the corner at the desired location, ensuring it is aligned with the previously installed siding or framing. Secure the corner using appropriate fasteners, ensuring even spacing and avoiding over-penetration. Apply sealant to the edges of the corner piece for added weather protection, creating a waterproof barrier. The corner should be tightly fitted to the adjacent siding to prevent gaps.
Trim Installation
Various trim pieces, such as window and door trim, are used to create a finished and aesthetically pleasing look around openings. These trim pieces should be carefully measured and cut to ensure a precise fit. Accurate cutting is critical to avoid gaps and ensure a seamless transition between the siding and the trim. The trim should be installed using appropriate fasteners and sealed with exterior-grade sealant to prevent water intrusion. Remember to maintain consistent spacing between fasteners for a secure and even installation.
Comparison of Trim Types
The following table compares different types of vinyl siding trim:
| Trim Type | Use | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| J-Channel | Starting and ending rows, around openings | Provides a finished edge and allows for expansion and contraction |
| Corner Trim | Exterior corners | Creates a neat and weathertight corner |
| Window and Door Trim | Around windows and doors | Provides a finished look and protects the openings |
| Soffit and Fascia Trim | Under eaves and around the roofline | Provides a finished look and protects the underlying structure |
Cutting and Fitting Trim Pieces
Accurate cutting of trim pieces is essential for a professional-looking installation. Use a sharp utility knife or a miter saw to ensure clean, precise cuts. For mitered corners, use a miter box or miter saw to achieve accurate 45-degree angles. Dry-fit the pieces before applying sealant and fasteners to ensure a proper fit. Remember to account for expansion and contraction of the vinyl material. Use a caulking gun to apply a bead of sealant along the joints to ensure a watertight seal. Overlapping joints should be sealed to prevent moisture penetration.
Finishing Touches and Inspections
Completing your vinyl siding installation involves more than just attaching the panels. Careful attention to detail in the final stages ensures a professional-looking and long-lasting result. This includes sealing gaps and seams, thoroughly cleaning the installation area, and performing a comprehensive inspection to identify and rectify any flaws. Proper maintenance after installation is also crucial for preserving the siding’s appearance and structural integrity.
The final steps are critical for achieving a watertight and aesthetically pleasing finish. Caulking properly seals gaps and prevents water damage, while cleaning removes any debris left over from the installation process. A thorough inspection allows for the prompt identification and correction of any mistakes, preventing larger issues down the line. Finally, establishing a regular maintenance schedule will help to prolong the life of your new vinyl siding.
Caulking and Cleaning
After installing all siding panels, trim, and accessories, it’s essential to caulk any gaps or seams to prevent water infiltration. Use a high-quality exterior-grade caulk in a color that matches your siding. Apply a thin, even bead of caulk to all joints, paying particular attention to areas around windows, doors, and corners. Allow the caulk to fully cure according to the manufacturer’s instructions before proceeding. Once the caulking is dry, thoroughly clean the entire siding surface. A soft brush and mild detergent solution are typically sufficient to remove any dirt, dust, or construction debris. Rinse thoroughly with clean water and allow the siding to dry completely.
Inspection Checklist
A systematic inspection is crucial to ensure the quality of your installation. This checklist helps identify potential problems early on, allowing for prompt correction and preventing future issues.
- Panel Alignment: Check for any misaligned or overlapping panels. They should be straight and evenly spaced.
- Caulk Integrity: Examine all caulked seams for gaps or cracks. Ensure complete coverage and proper adhesion.
- Fastener Visibility: Verify that all fasteners are properly concealed and not visibly protruding.
- Trim and Accessory Installation: Inspect all J-channels, corners, and trim for proper alignment and secure fastening.
- Water Drainage: Ensure that water will properly drain away from the house. Check for any potential areas of water accumulation.
- Overall Appearance: Step back and visually inspect the entire installation for any inconsistencies or imperfections.
Vinyl Siding Maintenance
Regular maintenance is key to preserving the beauty and longevity of your vinyl siding. A simple maintenance routine can prevent costly repairs and extend the lifespan of your investment. This includes regular cleaning and prompt attention to any damage.
- Regular Cleaning: Wash your siding at least once or twice a year using a garden hose and a soft brush or sponge. A mild detergent can be used for stubborn stains. Avoid high-pressure washers, as they can damage the siding.
- Prompt Repair: Address any damage, such as cracks or dents, immediately. Minor repairs can often be done with vinyl repair kits available at home improvement stores.
- Preventative Measures: Trim overhanging tree branches to prevent them from scratching the siding. Keep gutters clean to prevent water damage.
Safety Precautions During Installation
Vinyl siding installation, while seemingly straightforward, presents several potential hazards if proper safety precautions aren’t observed. Adhering to safety guidelines is crucial not only for preventing injuries but also for ensuring a successful and efficient installation process. Ignoring safety can lead to serious accidents, delays, and increased costs.
Safety during vinyl siding installation hinges on a combination of careful planning, the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and a thorough understanding of potential risks. This section details essential safety measures to protect yourself and others throughout the project.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Usage
Appropriate personal protective equipment is paramount to minimizing the risk of injury during vinyl siding installation. This equipment acts as a crucial barrier against potential hazards, protecting your body from harm.
- Safety Glasses or Goggles: These protect your eyes from flying debris, such as small pieces of siding or sharp metal scraps from cutting tools. The impact of even a small piece of debris can cause serious eye damage.
- Work Gloves: Gloves protect your hands from cuts, splinters, and abrasions that can occur when handling sharp materials or rough surfaces. They also offer protection against chemicals present in some cleaning agents used for surface preparation.
- Hearing Protection: Power tools, such as circular saws and nail guns, generate significant noise levels. Prolonged exposure to loud noise can lead to hearing loss. Ear plugs or muffs are essential for protecting your hearing.
- Respiratory Protection: If working in confined spaces or with materials that produce dust or fumes, a respirator is necessary to prevent inhalation of harmful particles. This is especially important when cutting or sanding materials.
- Footwear: Steel-toed boots provide protection against dropped objects and punctures. They also offer better stability on ladders and scaffolding.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation Strategies
Several hazards are inherent in vinyl siding installation. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies is vital for a safe working environment.
- Falls from Heights: Working at heights, especially on ladders or scaffolding, is a significant risk. Always use properly secured ladders and scaffolding, ensuring they are rated for the weight capacity and working height. Maintain three points of contact when climbing or working on ladders.
- Cuts and Punctures: Sharp edges of siding panels, cutting tools, and nails pose a risk of cuts and punctures. Always handle these materials carefully, using appropriate tools and gloves. Dispose of sharp waste properly.
- Electrocution: Contact with electrical wires or power lines is a serious hazard. Before beginning work, locate and mark all underground and overhead utility lines. Maintain a safe distance from any power lines.
- Exposure to the Elements: Work in extreme weather conditions can lead to heatstroke, hypothermia, or other weather-related illnesses. Avoid working in extreme heat or cold; schedule work during moderate weather conditions.
- Back Injuries: Lifting and carrying heavy materials can strain your back. Use proper lifting techniques and consider using mechanical lifting aids for heavier items.
Working Safely with Power Tools
Power tools are commonly used during vinyl siding installation. Safe operation of these tools is crucial to prevent injuries. Always ensure tools are properly maintained and in good working order before use.
- Proper Tool Usage: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for each tool. Use the correct blades, bits, and other accessories for the specific material being worked with.
- Secure Work Area: Ensure the work area is clear of obstructions and well-lit. Use clamps or other devices to secure materials during cutting or other operations.
- Disconnecting Power: Always disconnect power tools before making adjustments or changing blades.
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect power tools for damage or wear and tear. Replace worn parts promptly.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Problems
Even with careful planning and execution, problems can arise during vinyl siding installation. Understanding these common issues and their solutions is crucial for a successful project. This section outlines some frequently encountered problems and provides practical steps for resolving them, ensuring a professional-looking and durable finish.
Panel Gaps
Uneven gaps between vinyl siding panels are a common aesthetic issue. These gaps can result from improper measuring, cutting, or installation techniques. Large gaps compromise the weatherproofing of the siding.
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Uneven gaps between panels, exceeding manufacturer’s recommendations. | Carefully re-measure and cut panels to ensure proper fit. Check for consistent spacing using spacers. If necessary, remove and reinstall affected panels, ensuring proper overlap and alignment with the locking mechanism. |
| Gaps at panel ends, particularly noticeable near corners. | Ensure proper alignment of J-channels and corner pieces. Check that panels are fully seated and locked into place. If gaps persist, consider using additional trim pieces to conceal them. |
| Gaps appearing after temperature fluctuations. | This is often due to inadequate expansion and contraction allowance. Ensure proper spacing is maintained to accommodate temperature changes. Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for recommended expansion gaps. |
Panel Misalignment
Misaligned panels can significantly detract from the overall appearance of the siding. This often stems from errors in initial measurement or during the installation process itself.
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Panels not aligned vertically or horizontally. | Carefully check the alignment of each panel before securing it. Use a level to ensure straight lines. If misalignment occurs, remove and reinstall the affected panel(s). Work systematically to ensure correct alignment across the entire wall. |
| Panels overlapping unevenly. | Ensure proper overlap of each panel, following manufacturer’s guidelines for overlap measurements. This is crucial for water runoff and preventing leaks. |
| Panels buckling or warping. | This can be caused by improper installation, forcing panels into place, or exposure to extreme temperatures. Ensure panels are properly aligned and seated. If warping is significant, the panel may need replacement. |
Nail Holes and Damage
Visible nail holes or damaged panels detract from the finished look. Proper nailing techniques are essential to avoid these issues.
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Visible nail holes. | Use appropriately sized nails and a nail punch to set nails below the surface of the siding. Fill nail holes with vinyl caulk that matches the siding color. |
| Scratches or dents in the siding. | Minor scratches can often be buffed out with a soft cloth. For more significant damage, the affected panel may need replacement. |
Budgeting for a DIY Vinyl Siding Project
Undertaking a DIY vinyl siding project can significantly reduce costs compared to hiring professionals, but careful budgeting is crucial for success. This section outlines creating a realistic budget, strategies for saving money, and methods for accurately estimating material needs. Failing to plan properly can lead to unexpected expenses and project delays.
Sample Budget Breakdown for a Typical DIY Vinyl Siding Project
A comprehensive budget should account for all project expenses. The following is a sample breakdown for a 1500 square foot house, remembering that prices can vary significantly based on location, material choices, and project complexity.
| Expense Category | Estimated Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Vinyl Siding Panels | $3,000 – $6,000 | Cost varies greatly depending on quality, style, and color. |
| Underlayment/Sheathing | $500 – $1,000 | Essential for moisture protection and insulation. |
| J-Channels, Corners, and Trim | $500 – $1,000 | These finishing pieces are vital for a professional look. |
| Fasteners (Nails, Screws) | $100 – $200 | Choose high-quality fasteners for durability. |
| Caulk and Sealant | $50 – $100 | Necessary for weatherproofing. |
| Tools (Rental or Purchase) | $100 – $500 | Consider renting specialized tools if you won’t use them frequently. |
| Safety Equipment | $50 – $100 | Prioritize safety with proper gear like gloves, safety glasses, and a ladder. |
| Permits (if required) | $0 – $500 | Check local building codes for permit requirements. |
| Total Estimated Cost | $4,300 – $8,300 | This is a broad estimate; actual costs may vary. |
Strategies for Saving Money
Several strategies can help reduce costs without compromising quality.
Purchasing materials in bulk often results in lower per-unit costs. Consider buying from wholesale suppliers or during sales periods. Opting for a less expensive, yet still durable, vinyl siding grade can also save money. Careful planning and precise measurements minimize material waste, further reducing expenses. Finally, enlisting the help of friends or family for certain tasks can reduce or eliminate labor costs.
Estimating Material Quantities
Accurate material estimation is vital to avoid overspending or running short.
Begin by carefully measuring the total surface area of the walls to be sided. Consider using online calculators or consulting with a building supply store for assistance. Account for windows, doors, and other openings, subtracting their areas from the total wall area. Manufacturers usually provide coverage information per square foot on their packaging; this information will assist in calculating the number of panels needed. Always add extra material (approximately 10-15%) to account for cuts, mistakes, and potential damage.
To estimate siding quantity: Total wall area (square feet) x 1.10 (10% waste factor) = Estimated quantity of siding panels (square feet)
Ultimate Conclusion
Successfully installing vinyl siding requires careful planning, the right tools, and a methodical approach. By investing in high-quality tools, understanding the installation process, and following safety precautions, you can achieve a professional-looking result that adds value and curb appeal to your home. Remember, proper preparation and attention to detail are key to a long-lasting, beautiful finish. Now, go forth and transform your home’s exterior!