Comparing Siding Replacement Estimates from Different Contractors is a crucial step in any home renovation project. This process involves careful analysis of various factors, from pricing structures and labor costs to material quality and contractor reputation. Understanding these nuances can save homeowners significant time and money, ultimately ensuring a successful and satisfying outcome. This guide will walk you through a comprehensive comparison process, enabling informed decision-making.
By systematically examining the details presented in multiple estimates, homeowners can identify the best value proposition. This includes evaluating not only the upfront costs but also considering long-term factors such as material durability, warranty coverage, and the contractor’s overall experience and reliability. Making a well-informed choice contributes to a positive renovation experience and a lasting investment in your home.
Understanding the Estimates
Carefully reviewing multiple siding replacement estimates is crucial for making an informed decision. By comparing pricing structures, labor costs, and materials, you can identify the best value for your investment. This analysis focuses on three hypothetical estimates to illustrate the comparison process. Remember to replace these examples with your actual estimates.
Pricing Structures Comparison
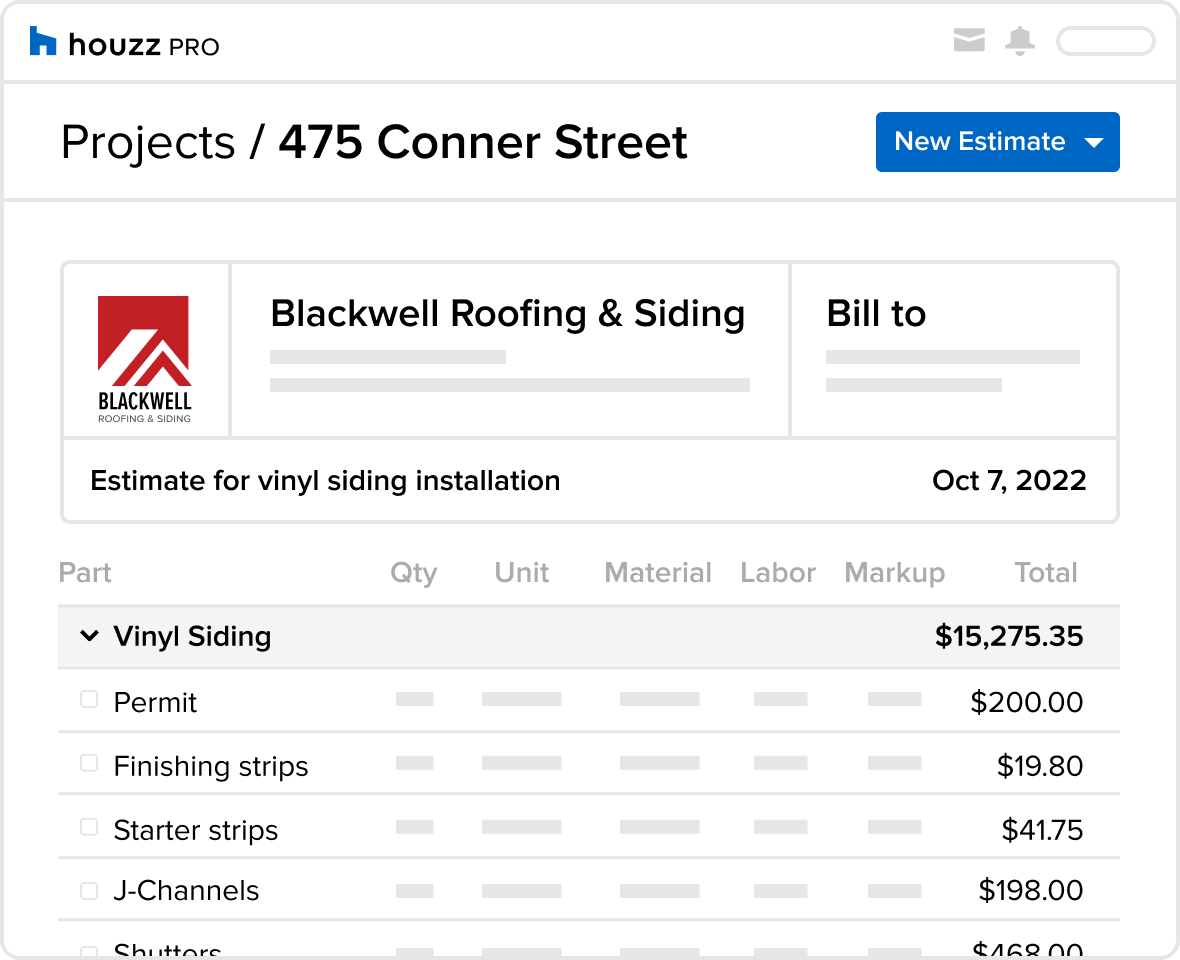
Three distinct pricing structures were observed in the hypothetical estimates. Contractor A provided a fixed-price quote, offering a single, all-inclusive price encompassing labor and materials. Contractor B offered a detailed breakdown of costs, separating labor, materials, and permitting fees. Contractor C used a square-foot pricing model, multiplying the area of the house needing siding by a per-square-foot cost, with separate line items for materials and labor. The fixed-price quote from Contractor A simplifies comparison but lacks transparency, while the detailed breakdown from Contractor B facilitates a comprehensive analysis. Contractor C’s approach is common but might not account for complexities in the project, potentially leading to unforeseen costs.
Labor Cost Breakdown
The labor cost breakdown varied significantly across the three estimates. Contractor A’s fixed-price quote included labor but didn’t specify the hourly rate or number of labor hours. Contractor B detailed labor costs as $15 per square foot, totaling $3,000 for a 200-square-foot project. This included preparation, installation, and cleanup. Contractor C estimated labor at $10 per square foot, totaling $2,000 for the same project, reflecting a potential difference in labor efficiency or skill level. These discrepancies highlight the importance of understanding the scope of work included in each labor cost.
Materials Used and Cost Impact
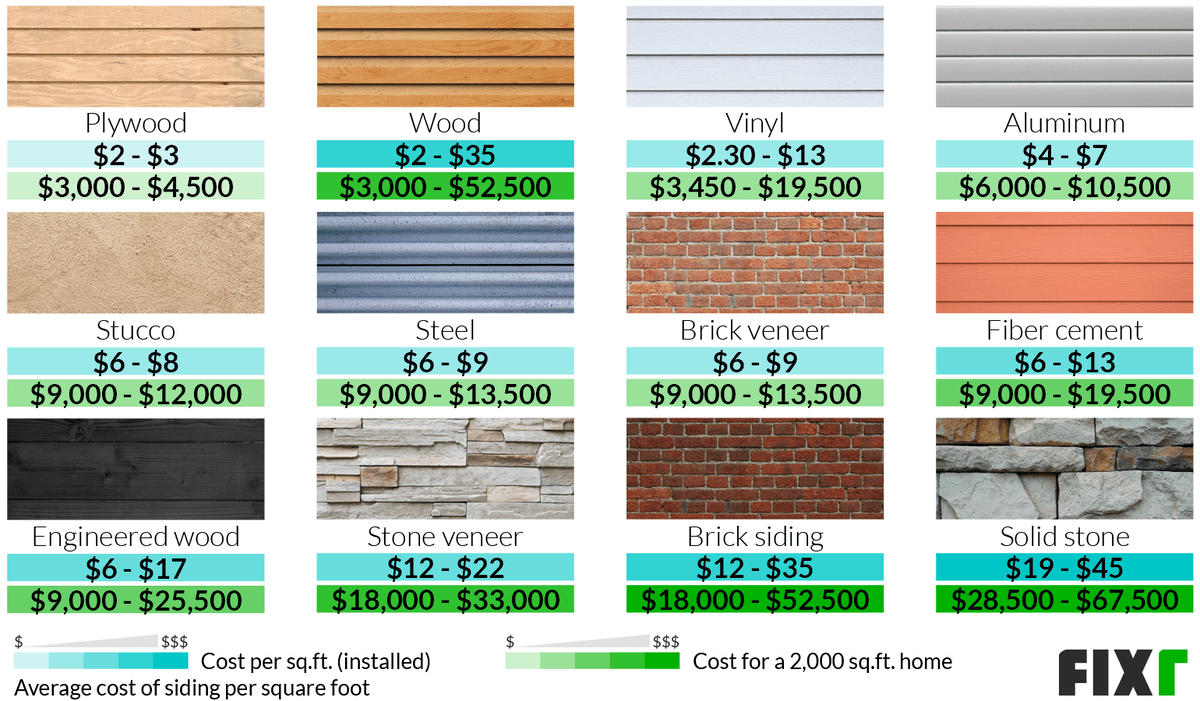
The estimates revealed differences in the types of siding materials proposed. Contractor A suggested using vinyl siding, a relatively inexpensive option, while Contractor B proposed fiber cement siding, a more durable but pricier choice. Contractor C recommended a premium cedar wood siding, leading to the highest material cost. The type of siding significantly impacts the overall cost. Vinyl siding (Contractor A) cost $5,000, fiber cement (Contractor B) $8,000, and cedar wood (Contractor C) $12,000 for the same 200-square-foot project. This difference reflects the varying durability, aesthetic appeal, and maintenance requirements of each material. Consider the long-term cost implications when comparing materials beyond initial price.
Analyzing Labor Costs
Labor costs represent a significant portion of your siding replacement project’s total expense. A thorough comparison of labor costs across different contractor estimates is crucial for making an informed decision. This analysis should consider not only the hourly rates and total labor hours but also the experience and qualifications of the work crews and the warranties offered on their workmanship.
Understanding the breakdown of labor costs allows for a more accurate assessment of value and helps identify potential discrepancies or areas of concern among competing bids. Factors such as crew size, projected project duration, and the complexity of the job all influence the final labor costs.
Hourly Rates and Total Labor Hours
Each contractor’s estimate should clearly detail the hourly rate charged for labor and the estimated number of hours required to complete the project. For example, Contractor A might quote $50 per hour for a crew of three workers, totaling 100 labor hours, while Contractor B might propose $60 per hour for a two-person crew, requiring 150 labor hours. Direct comparison reveals that Contractor A’s total labor cost ($15,000) is less than Contractor B’s ($9,000). However, a further investigation into the specifics of the work is necessary. Are the differing labor hours justified by the scope of work or project complexity? Does the higher hourly rate of Contractor B reflect a more skilled or experienced crew? These are important questions to consider.
Experience Level of Work Crews
The experience level of the installation crew significantly impacts the quality of the work and the overall project timeline. Look for details in the estimates about the crew’s experience with similar projects, their certifications (if applicable), and the average tenure of workers within the company. A contractor with a highly experienced and well-trained crew might justify a higher hourly rate due to increased efficiency and reduced risk of errors or rework. For example, Contractor C might highlight their team’s average of 10 years of experience in siding installation and their certifications from the relevant industry associations, indicating a higher level of expertise. Conversely, Contractor D might mention a younger, less experienced crew, potentially leading to a lower hourly rate but also a higher risk of mistakes or delays.
Labor Warranties and Guarantees
Scrutinize the warranties offered on the labor itself. A reputable contractor will typically provide a warranty covering their workmanship for a specific period, typically one to two years. This warranty should clearly outline what is covered (e.g., defects in installation, material failures due to installation errors), the duration of coverage, and the process for filing a claim. The length and comprehensiveness of the labor warranty can be a valuable indicator of the contractor’s confidence in their work and their commitment to customer satisfaction. For instance, Contractor E might offer a two-year warranty on all labor, while Contractor F might only offer a one-year warranty, suggesting a potential difference in confidence in their work or a less robust commitment to rectifying potential problems.
Material Specifications
Careful consideration of the siding materials proposed by each contractor is crucial for long-term value and aesthetic appeal. This section will compare the types and qualities of materials, manufacturer warranties, and the expected longevity and maintenance requirements of each option. This analysis will help you make an informed decision based on your budget and long-term goals.
Siding Material Comparison
Each contractor’s estimate should clearly specify the type of siding material being offered. Common options include vinyl, fiber cement, wood, and engineered wood. Vinyl siding is generally the most affordable, while fiber cement and wood offer superior durability and aesthetic appeal, but at a higher cost. Engineered wood siding combines the aesthetics of natural wood with enhanced durability and resistance to rot and insects. Direct comparison of the proposed materials – their manufacturer, specific product line, and color – is essential. For instance, one contractor might propose CertainTeed Monogram vinyl siding, while another might offer James Hardie fiber cement siding. These differences impact not only cost but also the overall look and longevity of your home’s exterior.
Manufacturer Warranties
The warranty offered by the siding manufacturer is a critical aspect to consider. Warranties typically cover defects in materials and workmanship, but the length and specific terms can vary significantly. Carefully review each warranty to understand its limitations. Some warranties might cover only the materials, while others might include labor. For example, a CertainTeed vinyl siding warranty might offer a 30-year limited warranty against defects, while a James Hardie fiber cement siding warranty could provide a 30-year non-prorated warranty against defects. Note that the contractor’s own warranty on installation will also be important, independent of the manufacturer’s warranty.
Siding Material Longevity and Maintenance
The longevity and maintenance requirements of different siding materials differ considerably. This table summarizes the typical lifespan and maintenance needs of common siding options:
| Siding Material | Typical Lifespan (Years) | Maintenance Requirements | Cost Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | 20-40 | Minimal; occasional cleaning | Low initial cost, potentially higher replacement cost over time |
| Fiber Cement | 50+ | Moderate; periodic painting or staining | Higher initial cost, lower long-term replacement cost |
| Wood | 20-50 (depending on species and treatment) | High; regular painting, staining, and potential repairs | High initial cost, potentially high maintenance costs |
| Engineered Wood | 30-50 | Moderate; periodic cleaning and occasional repainting | Medium initial cost, moderate maintenance costs |
Payment Terms and Financing Options
Choosing the right siding contractor often involves careful consideration of not only the quality of materials and workmanship but also the payment structure. Understanding the payment terms and financing options offered by different contractors is crucial for budgeting and ensuring a smooth project completion. This section will compare the various payment schedules and financing options to help you make an informed decision.
Payment schedules vary significantly among contractors. Some may require a large upfront deposit, while others might prefer staged payments tied to project milestones. Understanding these differences is vital for managing your cash flow effectively. Financing options, if available, can ease the financial burden of a large home improvement project. However, it’s important to compare interest rates and repayment terms to choose the most suitable option.
Payment Schedules
Contractors typically outline their payment schedules in the contract. These schedules often involve a down payment, progress payments at various stages of the project (e.g., after material delivery, after completion of framing, after installation), and a final payment upon project completion and your satisfaction. For example, one contractor might require 20% upfront, 30% upon completion of the framing, 30% upon installation, and 20% final payment. Another might opt for a 50% deposit and the remaining 50% upon completion. It’s vital to compare these structures and ensure they align with your budget and payment capabilities.
Financing Options
Several contractors offer financing options, often partnering with financial institutions to provide loans specifically for home improvement projects. These loans typically come with interest rates and repayment terms. For instance, a contractor might offer a 0% interest loan for 12 months, or a loan with a fixed interest rate over several years. It’s important to review the terms and conditions of any financing offer, including the Annual Percentage Rate (APR), any associated fees, and the total cost of the loan over its lifespan. Always compare these offers from different contractors and with other financing options available to you independently.
Upfront Costs and Deposits
The upfront cost, usually a deposit or down payment, serves as a commitment from the homeowner and often covers initial materials procurement or project preparation. The percentage of the total project cost required as a deposit varies greatly. A high deposit may indicate a contractor’s confidence in their work, but it can also place a significant burden on the homeowner’s finances. Lower deposits might seem attractive but could indicate a less established contractor or a higher risk of project delays. Thoroughly review the contract to understand what the deposit covers and what recourse you have if the project is not completed as agreed.
Late Payment Penalties
Most contractor contracts stipulate penalties for late payments. These penalties can range from late fees (a fixed amount or a percentage of the outstanding balance) to interest charges or even suspension of work until the outstanding payment is received. Understanding the specific late payment penalties outlined in each contract is crucial to avoid unexpected financial repercussions. For example, a contract might state a late payment fee of $50 per day or an interest rate of 1.5% per month on overdue payments. It is advisable to plan carefully to avoid any late payment situations.
Contractor Experience and Reputation
Choosing a contractor for your siding replacement is a significant investment, and their experience and reputation play a crucial role in ensuring a successful project. Thoroughly investigating a contractor’s history and client feedback is essential to making an informed decision. This section compares the experience and reputation of the contractors you’ve received estimates from.
This analysis considers several key factors to assess the reliability and trustworthiness of each contractor. We will examine their years of experience in siding installation, relevant certifications and licenses, and the feedback provided by previous clients. A comprehensive review of these factors allows for a more objective comparison.
Contractor Experience and Certifications
The following table summarizes the years of experience and relevant certifications held by each contractor. This information is crucial in determining their level of expertise and adherence to industry best practices. Note that the presence of certifications does not guarantee superior workmanship, but it indicates a commitment to professional standards.
| Contractor Name | Years of Experience | Certifications/Licenses |
|---|---|---|
| ABC Siding Solutions | 15 years | Certified Residential Contractor (CRC), Licensed in [State] |
| XYZ Home Improvements | 8 years | Licensed in [State] |
| 123 Exterior Renovations | 20 years | Certified Siding Installer (CSI), Licensed in [State], A+ rating with the Better Business Bureau |
Online Reviews and Customer Testimonials
Examining online reviews and testimonials offers valuable insights into past client experiences. These reviews provide a firsthand account of the contractor’s professionalism, workmanship, communication, and overall project management. While individual experiences can vary, a consistent pattern of positive or negative feedback can be indicative of a contractor’s reliability.
Below is a summary of online reviews for each contractor. Note that the number of reviews and the overall rating are taken from [Platform Name, e.g., Google Reviews, Yelp] as of [Date].
- ABC Siding Solutions: Average rating of 4.5 stars out of 5 based on 75 reviews. Positive comments frequently mentioned excellent communication and attention to detail. Negative comments were rare and generally related to minor scheduling delays.
- XYZ Home Improvements: Average rating of 3.8 stars out of 5 based on 30 reviews. Positive comments praised the competitive pricing. Negative comments cited occasional communication issues and minor quality control problems.
- 123 Exterior Renovations: Average rating of 4.8 stars out of 5 based on 150 reviews. Consistently high praise for professionalism, quality of work, and customer service. Few negative comments were reported, mostly addressing minor issues promptly resolved.
Contractor Pros and Cons
Based on the analysis of experience, certifications, and online reviews, the following summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of each contractor:
- ABC Siding Solutions:
- Pros: Solid experience, good communication, generally positive reviews.
- Cons: Occasional minor scheduling delays reported.
- XYZ Home Improvements:
- Pros: Competitive pricing.
- Cons: Communication issues and minor quality control problems reported in some reviews.
- 123 Exterior Renovations:
- Pros: Extensive experience, multiple certifications, overwhelmingly positive reviews, excellent reputation.
- Cons: None significant reported.
Project Timeline and Scheduling
The project timeline is a critical factor when comparing siding replacement estimates. A shorter timeline might seem appealing, but it’s crucial to understand the implications of rushed work versus a more deliberate approach. Contractors’ schedules should align with your availability and any other relevant factors, such as weather conditions.
Understanding the proposed timelines from different contractors allows for a comprehensive comparison, enabling you to choose the contractor best suited to your needs and preferences. Delays can significantly impact your budget and overall project satisfaction. Careful consideration of potential delays is essential for a smooth and successful siding replacement.
Estimated Project Timelines
Each contractor’s estimate should clearly outline the expected project duration, broken down into phases if possible (e.g., demolition, installation, cleanup). Compare these timelines directly. For example, Contractor A might estimate completion in 7 days, while Contractor B proposes 10 days. These differences may be due to various factors including crew size, project complexity, and scheduling efficiency. A detailed breakdown of each phase’s duration can provide a more nuanced understanding.
Potential Delays and Unforeseen Circumstances
Several factors can cause delays. Unexpected weather conditions (heavy rain, extreme heat, or snow) can significantly impact outdoor work. Discovering unforeseen issues during demolition, such as rotted wood or damaged sheathing, may require additional time for repairs. Supply chain disruptions could delay the arrival of materials. Finally, unforeseen scheduling conflicts within the contractor’s team could also lead to delays. A reputable contractor will proactively communicate potential delays and offer solutions to mitigate their impact. For example, a delay caused by material shortage might be offset by prioritizing other tasks.
Project Timeline Comparison Chart
| Contractor | Total Project Time (Days) | Demolition (Days) | Installation (Days) | Cleanup (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contractor A | 7 | 1 | 5 | 1 |
| Contractor B | 10 | 2 | 7 | 1 |
| Contractor C | 9 | 1.5 | 6.5 | 1 |
| Contractor D | 12 | 2 | 8 | 2 |
Permits and Licenses
Obtaining the necessary permits and ensuring your contractor is properly licensed and insured are crucial steps in a successful siding replacement project. These aspects significantly impact the legality, safety, and overall quality of the work. A thorough comparison of these elements across different contractor estimates is essential before making a final decision.
Permit costs and licensing information should be clearly outlined in each estimate. The absence of these details can indicate a potential lack of professionalism or even illegal operation. Understanding the implications of missing permits and licenses is vital to avoid future complications and potential legal liabilities.
Permit Costs and Inclusion
Each estimate should explicitly state the costs associated with obtaining the necessary permits. These costs can vary depending on your location, the scope of the project, and the specific permits required. For example, a larger project involving significant structural changes might require more permits and incur higher costs compared to a smaller, simpler job. Compare the breakdown of permit fees provided by each contractor. Discrepancies should prompt further investigation to ensure accuracy and transparency. Some contractors may include permit fees in their overall price, while others may list them separately. Clarify this detail with each contractor to avoid unexpected expenses.
Contractor Licensing and Insurance
Verify that each contractor holds the necessary licenses and insurance to perform the work. This typically includes a general contractor’s license and liability insurance. Request copies of these documents to confirm their validity and coverage. Estimates should clearly state the contractor’s licensing information and insurance policy details, including the policy number and the insurance company’s contact information. The absence of proper licensing and insurance exposes you to significant risks, including potential liability for accidents or damages during the project. Insufficient insurance coverage could leave you financially responsible for unforeseen events.
Obtaining Necessary Permits
The process of obtaining building permits generally involves submitting an application to your local building department along with detailed plans and specifications for the project. This application often requires information about the materials being used, the scope of work, and the contractor’s licensing information. The building department will review the application and plans to ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations. Once approved, you will receive a permit that allows the contractor to legally commence the work. The timeline for permit approval can vary depending on the complexity of the project and the efficiency of the local building department. In some cases, the contractor may handle the permit application process, while in others, the homeowner may be responsible. Clarify who is responsible for obtaining the permits and the associated timeline with each contractor. Delays in obtaining permits can significantly impact the project timeline, so factor this into your decision-making process.
Warranties and Guarantees
Understanding the warranties offered by different siding contractors is crucial for protecting your investment. A comprehensive warranty provides peace of mind and safeguards against potential defects or issues that may arise after installation. Comparing warranties allows you to make an informed decision based on the level of protection each contractor provides.
Thoroughly reviewing the warranty documents provided by each contractor is essential. Pay close attention to the specific terms, conditions, and limitations of each warranty to ensure you understand the extent of coverage. Note that warranties often vary in their length and the types of issues they cover.
Warranty Duration and Coverage
The duration of warranties varies significantly between contractors and even between the materials and labor components of the project. Some manufacturers offer lifetime warranties on their siding products, while others provide shorter, limited warranties, typically ranging from 10 to 20 years. Labor warranties usually cover a shorter period, often ranging from 1 to 5 years. It’s vital to note whether these warranties are transferable to future homeowners if you plan to sell your property in the near future. For example, Contractor A might offer a 25-year warranty on their vinyl siding and a 2-year warranty on their labor, while Contractor B might offer a 15-year warranty on their fiber cement siding and a 1-year warranty on their labor.
Warranty Limitations and Exclusions
Warranties are not always absolute. Many contain specific limitations and exclusions that restrict their coverage. Common exclusions include damage caused by acts of God (such as hurricanes or floods), improper maintenance by the homeowner, or damage resulting from modifications or alterations made to the siding after installation. Some warranties might also exclude certain types of defects, such as minor cosmetic imperfections. For example, a warranty might cover major structural defects but exclude minor scratches or discoloration. Carefully reviewing these limitations is essential to avoid misunderstandings or disputes later. Understanding these limitations will help you assess the true value and protection offered by each warranty.
Comparison of Contractor Warranties
To facilitate comparison, consider creating a table summarizing the key features of each contractor’s warranty. This table could include columns for contractor name, material used, material warranty duration, material warranty exclusions, labor warranty duration, and labor warranty exclusions. This organized comparison will highlight the differences and allow for a clearer understanding of the overall value proposition of each contractor’s offer. For instance, a table might show that Contractor A’s warranty covers material defects for 25 years and labor for 2 years, excluding damage from extreme weather events, while Contractor B’s warranty covers material defects for 15 years and labor for 1 year, with similar exclusions.
Cleanup and Waste Disposal
Careful consideration of cleanup and waste disposal procedures is crucial when comparing siding replacement estimates. Contractors should detail their methods for managing debris and ensuring a clean worksite throughout and after the project. Differences in these approaches can significantly impact the overall cost and the level of disruption to your property.
Waste and debris removal methods vary considerably between contractors. Some may use dumpsters placed strategically on your property, while others might opt for smaller, more frequent pickups. The frequency of waste removal directly affects the cleanliness of your property during the project. Furthermore, the method of disposal itself—landfill versus recycling—can impact both cost and environmental responsibility. It is important to ascertain whether the contractor’s methods align with your preferences and local environmental regulations.
Waste Removal Methods
Contractors should clearly outline their plan for handling construction debris. This should include details on the type of containers used (dumpsters, smaller bins), the frequency of removal, and the disposal method employed. For example, one contractor might describe using a large dumpster for the duration of the project, while another might detail a system of daily or bi-daily smaller container removal. This information allows for a direct comparison of approaches and associated costs. Inquire about the contractor’s commitment to recycling and responsible waste management practices. A responsible contractor will clearly state their commitment to minimizing environmental impact.
Responsibility for Cleanup
The contract should explicitly state the contractor’s responsibility for cleanup and waste disposal. This typically includes the removal of all construction debris, including scrap siding, packaging materials, and leftover building supplies. However, it’s important to clarify whether the contractor is responsible for cleaning areas beyond the immediate project site, such as driveways or walkways. Some contractors may offer additional cleaning services at an extra cost. A clear understanding of these responsibilities prevents misunderstandings and potential disputes after the project’s completion. A detailed breakdown of these responsibilities should be included in the written contract.
Addressing Project-Related Damage
Any damage incurred during the siding replacement process should be addressed by the contractor. This might include damage to landscaping, gutters, or other exterior features. Reputable contractors will have procedures in place to document, assess, and repair any accidental damage. The contractor’s estimate should ideally include a contingency for unforeseen damage, or at least clearly outline the process for handling such situations. For instance, a contractor might provide photographic documentation of existing conditions before commencing work, serving as a baseline for comparison after project completion. If damage does occur, a responsible contractor will promptly address it to the homeowner’s satisfaction.
Total Project Cost and Value
Comparing siding replacement estimates requires a thorough analysis of the total project cost and the value each proposal offers. This involves not only looking at the bottom line price but also understanding what contributes to that price and the long-term benefits each option provides. A lower upfront cost might seem attractive, but it could ultimately prove more expensive if the materials are inferior or the warranty inadequate.
The total cost encompasses materials, labor, permits, and any other associated fees. The value proposition, however, considers the quality of materials, the experience and reputation of the contractor, the length and comprehensiveness of the warranty, and the overall expected lifespan of the new siding. By carefully weighing these factors, you can determine which estimate offers the best combination of cost and value.
Comparative Analysis of Estimates
To effectively compare, organize the information from each estimate into a clear format. This will help you easily identify key differences and advantages. Consider creating a table like the one below, which summarizes the key aspects of each estimate received. Remember to replace the example data with your own.
| Contractor | Total Cost | Material Type | Warranty Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC Siding | $15,000 | Vinyl Siding – Premium Grade | 25 Years |
| XYZ Construction | $12,000 | Vinyl Siding – Standard Grade | 10 Years |
| 123 Home Improvements | $18,000 | Fiber Cement Siding | 30 Years |
Value Proposition Assessment
Each estimate’s value proposition depends on individual priorities. For example, ABC Siding offers a premium-grade vinyl siding with a long warranty, suggesting higher quality and longer lifespan, justifying the higher price. XYZ Construction’s lower price reflects the use of standard-grade vinyl siding and a shorter warranty, implying a potentially shorter lifespan and higher risk of future repairs. 123 Home Improvements offers a higher initial investment but uses durable fiber cement siding with an extended warranty, indicating superior long-term value despite the higher upfront cost. The choice depends on your budget and your desired balance between initial cost and long-term durability.
End of Discussion
Ultimately, comparing siding replacement estimates requires a multifaceted approach. By carefully considering the elements discussed – pricing, labor, materials, contractor reputation, timelines, and warranties – homeowners can make a confident and informed decision. Choosing the right contractor and siding materials will not only enhance your home’s curb appeal but also ensure long-term value and peace of mind. Remember, a thorough comparison empowers you to make the best choice for your home and budget.