Budgeting for a Full Home Siding Replacement is a crucial step in any home renovation project. This process involves careful consideration of various factors, from material costs and labor expenses to permits, unexpected repairs, and financing options. Understanding these elements ensures a smooth and financially responsible renovation, transforming your home’s exterior and potentially increasing its value. This guide will walk you through each stage, providing valuable insights and practical advice to help you navigate the budgeting process with confidence.
We will explore the cost differences between various siding materials like vinyl, wood, and fiber cement, highlighting the long-term cost-effectiveness of each. We’ll also delve into the complexities of labor costs, contractor selection, and permit acquisition, offering strategies for finding reliable contractors and navigating the permitting process efficiently. Furthermore, we’ll address potential hidden costs, contingency planning, and financing options to ensure you’re fully prepared for the financial aspects of your siding replacement.
Understanding Material Costs
Replacing your home’s siding is a significant investment, and understanding the material costs is crucial for accurate budgeting. The price of siding varies considerably depending on the material chosen, its quality, and regional factors. This section will break down the costs of common siding materials and discuss their long-term value.
Typical Siding Material Costs
Several factors influence the final cost of siding materials. These include the type of siding, its quality (e.g., thickness, durability ratings), the style and color chosen, and regional variations in material availability and labor rates. Additionally, the complexity of your home’s design, such as the number of angles, dormers, and other architectural features, will affect the overall material needs and, consequently, the final cost. Premium materials and finishes will naturally command higher prices.
Cost Comparison of Siding Materials
Choosing the right siding material involves weighing initial costs against long-term maintenance and lifespan. Vinyl siding is generally the most affordable upfront, but may not last as long as other options. Wood siding offers a classic look but requires significant ongoing maintenance to prevent rot and insect damage. Fiber cement provides excellent durability and longevity, but comes with a higher initial price tag. Metal siding, while durable, can be susceptible to dents and may be more expensive than vinyl but less so than fiber cement.
Cost Per Square Foot of Various Siding Materials
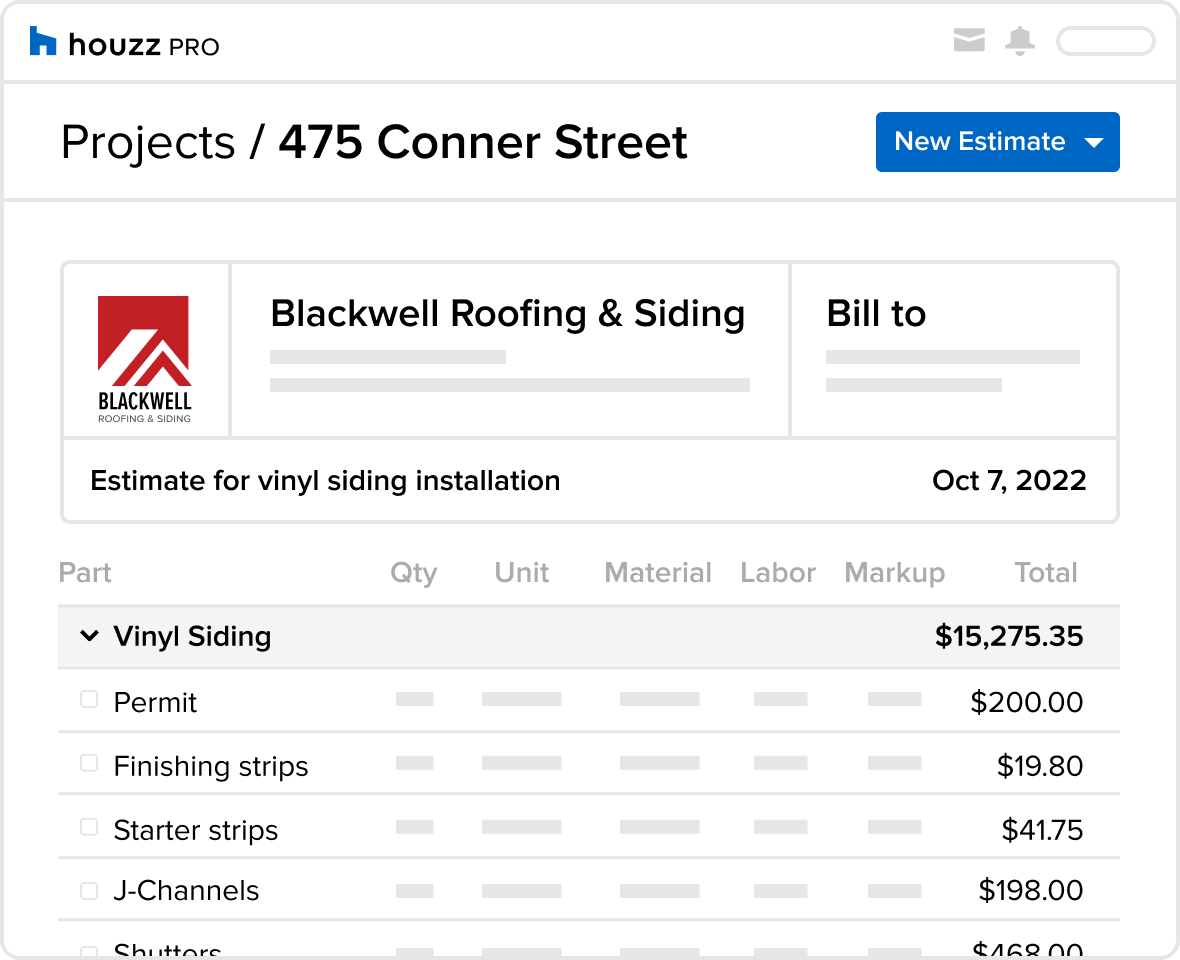
The following table provides estimated costs per square foot for various siding materials, including both material and installation costs. These figures are averages and can vary based on location, installer, and material specifics. It’s crucial to obtain multiple quotes from reputable contractors in your area for accurate pricing.
| Siding Material | Material Cost ($/sq ft) | Installation Cost ($/sq ft) | Total Cost ($/sq ft) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | $2 – $6 | $3 – $5 | $5 – $11 |
| Wood | $6 – $15 | $5 – $10 | $11 – $25 |
| Fiber Cement | $8 – $18 | $6 – $12 | $14 – $30 |
| Metal | $7 – $15 | $5 – $8 | $12 – $23 |
Labor Costs and Contractor Selection
Replacing your home’s siding is a significant investment, and labor costs represent a substantial portion of the total expense. Understanding the factors that influence these costs and employing effective strategies for contractor selection are crucial for a successful and budget-friendly project. This section will explore these key aspects to help you navigate this important phase of your home improvement project.
Labor costs for siding replacement are influenced by several interconnected factors. The size of your home directly impacts the time and effort required, with larger homes naturally demanding more labor hours. The complexity of the project also plays a significant role. Homes with intricate architectural details, multiple stories, or difficult-to-access areas will necessitate more skilled labor and thus, higher costs. Finally, geographical location influences labor rates. Areas with high costs of living or a shortage of skilled tradespeople tend to have higher labor rates for construction projects. For example, a siding replacement project in a densely populated urban area might cost considerably more than a similar project in a rural region due to higher demand and overhead costs for contractors.
Factors Influencing Labor Costs
Several key factors contribute to the overall labor costs associated with siding replacement. Project size, measured in square footage, directly correlates with the number of labor hours required. More complex projects, involving intricate designs, multiple materials, or significant repairs to underlying structures, will naturally command higher labor costs due to increased time and specialized skills needed. The geographical location of the property also plays a crucial role; areas with higher labor costs due to factors such as high demand or local regulations will translate to a higher price tag for the labor component of the project. For instance, a coastal region might have higher labor rates due to a combination of high demand and potentially more stringent building codes. Finally, the type of siding chosen also influences labor costs. Certain materials, such as intricate stone veneer, require more specialized skills and time to install than simpler vinyl siding, resulting in a higher labor expense.
Strategies for Finding Reliable and Reasonably Priced Contractors
Securing a reliable and reasonably priced contractor is paramount. Begin by requesting referrals from friends, family, or neighbors who have recently undergone similar projects. Online reviews and ratings on platforms like Yelp or Angie’s List can also provide valuable insights into contractors’ reputations and past performance. It is crucial to obtain at least three detailed bids from different contractors to compare pricing and services. During the bidding process, ensure the bids clearly outline all included materials, labor costs, and any additional fees. Verify that the contractors are properly licensed, insured, and have a proven track record of successful projects.
Contractor Bidding Processes and Contract Structures
Contractors typically employ different bidding processes. Some provide fixed-price bids, outlining a total cost for the entire project. Others might offer time-and-materials bids, where the final cost is determined by the actual labor hours and materials used. Fixed-price bids offer greater cost certainty, but they might not account for unforeseen complications. Time-and-materials bids offer flexibility but could potentially lead to higher-than-anticipated costs if the project encounters unexpected challenges. Regardless of the bidding process, the contract should clearly specify the scope of work, payment schedule, timelines, and warranty provisions. Thoroughly reviewing the contract before signing is crucial to protect your interests and ensure a clear understanding of the agreement between you and the contractor. A well-structured contract will clearly define the responsibilities of both parties, outlining payment milestones and addressing potential disputes. It should also include details about permits, insurance coverage, and the warranty period for the completed work. Consider consulting with a legal professional to review the contract before signing, especially for large-scale projects.
Permits and Inspections
Securing the necessary permits and passing inspections are crucial steps in any home siding replacement project. These processes ensure your project complies with local building codes and regulations, protecting both your investment and the safety of your property. Failure to obtain the correct permits can lead to significant fines, delays, and even the need to undo completed work.
Obtaining building permits for a siding replacement typically involves submitting an application to your local building department. This application usually requires detailed plans, specifications of the materials to be used, and sometimes even a contractor’s license number. The review process can vary in length depending on the complexity of the project and the workload of the building department.
Permitting Process
The permitting process generally begins with submitting a complete application to your local building department. This application will include detailed information about the project, including the type of siding, the area to be covered, and any structural modifications involved. After the application is reviewed, the department may schedule an inspection of your property to verify the information provided. Upon approval, you’ll receive your permit. This permit grants you legal authorization to proceed with the project. Any work performed without a permit is considered illegal and subject to penalties. It’s important to keep copies of all permits and inspection reports for your records.
Permit and Inspection Costs
The cost of permits and inspections varies considerably depending on location, project scope, and the complexity of the work. Permit fees are usually calculated based on factors such as the square footage of the siding to be replaced and the type of materials used. Inspection fees are often charged per inspection, with multiple inspections required at various stages of the project. For example, a typical permit fee for a mid-sized home siding replacement might range from $200 to $1000, while inspection fees could add another $100 to $500. It’s advisable to contact your local building department for a precise estimate based on your specific project details.
Potential Delays and Complications
Several factors can cause delays or complications during the permitting process. Incomplete applications, missing documentation, or discrepancies between the application and the actual project can lead to significant delays. Furthermore, unusually high workloads at the building department, changes in local regulations, or unforeseen issues discovered during inspections can also extend the timeline. In some cases, appeals or disputes may arise if the building department denies a permit, further delaying the project. For example, a homeowner might experience a delay of several weeks if they need to resubmit corrected plans or if the building department’s workload is unexpectedly high. Proactive communication with the building department and careful preparation of the application are crucial to minimize potential delays.
Hidden Costs and Contingencies
Replacing your home’s siding is a significant undertaking, and while careful planning helps minimize expenses, unforeseen costs can significantly impact your budget. Understanding these potential hidden costs and implementing strategies to account for them is crucial for a successful and stress-free project. Failing to plan for contingencies can lead to project delays, budget overruns, and even compromise the quality of the finished work.
Unexpected expenses during a siding replacement project are common. These costs often stem from issues discovered only after the project has begun, requiring additional work and materials. Thorough planning, including a contingency budget, helps mitigate the financial impact of these surprises.
Examples of Unexpected Costs
Discovering underlying problems during siding removal is a frequent source of unexpected expenses. For example, extensive rotted wood under the existing siding may require significant repair or replacement before new siding can be installed. This could involve replacing damaged sheathing, adding additional structural support, or even addressing underlying moisture problems. Similarly, foundation issues, such as cracks or settling, might be revealed, requiring costly repairs before the siding installation can proceed. Other unexpected costs might include the discovery of lead paint under the old siding, necessitating specialized removal procedures that comply with environmental regulations. Unexpectedly high material costs due to supply chain issues or material shortages can also occur, particularly during periods of high demand. Finally, unforeseen site conditions, such as difficult terrain or the presence of underground utilities that require additional safety measures, could lead to increased labor costs.
Strategies for Budgeting for Unforeseen Expenses
A proactive approach to budgeting for unforeseen expenses involves adding a contingency to your overall project cost. This contingency should be a percentage of the total estimated cost, typically ranging from 10% to 20%, depending on the complexity of the project and the age of the home. A higher percentage is advisable for older homes or those with known potential issues. Detailed pre-project inspections by a qualified contractor can help to refine this percentage and identify potential problem areas early on. Regular communication with your contractor throughout the project allows for early identification of potential cost overruns and the development of solutions to keep the project on track. Maintaining a detailed record of all expenses, including receipts and change orders, ensures transparency and facilitates accurate financial tracking. Finally, securing sufficient funding before commencing the project, including the contingency budget, protects you from unexpected financial strain.
Sample Contingency Budget
Let’s assume a total estimated cost for a siding replacement project is $15,000. Using a conservative contingency of 15%, the contingency budget would be $2,250. This contingency fund could be allocated as follows:
| Contingency Item | Allocated Amount |
|---|---|
| Wood Repair/Replacement | $750 |
| Foundation Repair (minor) | $500 |
| Lead Paint Removal (if necessary) | $500 |
| Unexpected Material Cost Increases | $500 |
Note: This is a sample budget and the actual allocation will vary depending on the specific circumstances of your project.
Financing Options
Replacing your home’s siding is a significant investment. Securing the necessary funds can be a crucial step in the process. Several financing options exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these options will help you choose the best fit for your financial situation and project needs.
Financing your siding replacement project typically involves securing a loan to cover the upfront costs. The repayment schedule and interest rates will significantly impact your overall expenses. Careful consideration of these factors is essential to avoid financial strain.
Home Equity Loans
Home equity loans utilize the equity you’ve built in your home as collateral. This means you borrow against the difference between your home’s value and the amount you still owe on your mortgage. These loans typically offer fixed interest rates and fixed monthly payments, making budgeting easier. However, it’s crucial to remember that you risk losing your home if you default on the loan. The interest rates are usually lower than those of personal loans due to the lower risk for the lender. For example, a homeowner with substantial equity might secure a home equity loan at a rate of 6%, significantly lower than a personal loan’s potential rate of 12% or higher.
Personal Loans
Personal loans are unsecured loans, meaning they don’t require collateral. This makes them accessible to individuals who may not qualify for a home equity loan or prefer not to risk their home. However, the interest rates on personal loans are generally higher than home equity loans, reflecting the increased risk for the lender. The repayment terms are also variable, depending on the lender and the borrower’s creditworthiness. A personal loan might offer a higher interest rate, such as 10-15%, but its accessibility makes it a viable option for those with limited equity or less-than-perfect credit.
Credit Cards
Using a credit card can be a convenient short-term solution for smaller siding projects or unexpected costs. However, this method carries the highest interest rates and should be avoided for larger projects due to the accumulating debt and high interest charges. It’s generally advisable to use this option only for smaller, unforeseen expenses during the project and not as primary financing.
Comparison of Financing Options
| Financing Option | Interest Rate | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Equity Loan | Generally lower (e.g., 6%) | Lower interest rates, fixed payments, potentially tax deductible | Requires home equity, risk of foreclosure |
| Personal Loan | Generally higher (e.g., 10-15%) | No collateral required, accessible to a wider range of borrowers | Higher interest rates, less favorable terms |
| Credit Cards | Very high (e.g., 18-25%) | Convenient for small expenses | Extremely high interest rates, potential for significant debt accumulation |
Project Timeline and Scheduling
Planning a realistic timeline for your home siding replacement is crucial for managing expectations and avoiding delays. A well-defined schedule helps ensure the project progresses smoothly and minimizes disruptions to your daily life. Understanding the factors that can influence the timeline allows for proactive adjustments and mitigates potential problems.
A typical home siding replacement project can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on several key factors. The size of the house, the complexity of the design, and the chosen materials all play a significant role in determining the overall duration. Furthermore, unforeseen circumstances can extend the timeline, highlighting the importance of building in buffer time.
Factors Affecting Project Timeline
Several factors can significantly influence the duration of a siding replacement project. These factors range from predictable elements like weather conditions to less predictable ones such as material availability. Accurate project planning requires careful consideration of these potential delays.
- Weather Conditions: Inclement weather, such as heavy rain, snow, or extreme heat, can cause significant delays. Exterior work is often weather-dependent, and prolonged periods of unsuitable weather can push back the project schedule considerably. For example, a project planned for the rainy season in a region with frequent downpours might experience several weeks of delays.
- Material Availability: Delays in material delivery can occur due to supply chain issues, manufacturer backlogs, or transportation problems. Specifying uncommon or specialized siding materials might increase the risk of delays compared to using readily available options. For instance, a project requiring a specific type of imported cedar siding might face delays if shipments are delayed due to port congestion.
- Contractor Availability and Scheduling: The contractor’s existing workload and scheduling conflicts can influence the project timeline. Choosing a contractor who is already overcommitted might lead to delays as they juggle multiple projects. Similarly, unexpected issues or emergencies arising on other projects may impact their availability for your project.
- Permitting and Inspection Processes: Obtaining necessary permits and scheduling inspections can sometimes take longer than anticipated, especially if there are unforeseen complications or bureaucratic delays. Lengthy review processes or required revisions to submitted plans can significantly extend the overall project timeline.
- Unexpected Issues: Unforeseen problems, such as discovering rotted wood under the existing siding or encountering unexpected structural issues, can necessitate additional work and extend the project schedule. Thorough inspections prior to commencement can help minimize these surprises, but they are not always entirely preventable.
Sample Project Schedule
The following sample schedule illustrates a potential timeline for a medium-sized home siding replacement project. This schedule assumes favorable weather conditions and readily available materials. It is crucial to remember that this is a sample, and individual projects will vary significantly.
| Phase | Milestone | Estimated Duration | Start Date (Example) | End Date (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Permit Acquisition & Site Survey | 1-2 weeks | October 23rd | November 5th |
| Demolition | Removal of Existing Siding | 1 week | November 6th | November 12th |
| Preparation & Repair | Underlayment Installation & Repairs | 1 week | November 13th | November 19th |
| Installation | New Siding Installation | 2-3 weeks | November 20th | December 7th |
| Finishing | Final Inspection & Cleanup | 1 week | December 8th | December 14th |
Waste Removal and Disposal
Replacing your home’s siding generates a significant amount of waste, and proper disposal is crucial for both budgetary and environmental reasons. This section details the costs associated with waste removal, environmentally sound disposal practices, and relevant local regulations. Failing to plan for waste removal can lead to unexpected expenses and potential legal issues.
Proper disposal of old siding materials is essential for environmental protection and compliance with local regulations. The costs associated with this process vary depending on several factors, including the type and quantity of waste, the distance to the disposal site, and the chosen disposal method. Understanding these factors is key to accurately budgeting for your siding replacement project.
Costs Associated with Waste Removal and Disposal
The cost of waste removal and disposal for a siding replacement project can range considerably. Factors influencing the final cost include the volume of waste generated (determined by the size of your home and the type of siding being removed), the type of waste (e.g., wood, vinyl, asbestos), and the distance the waste needs to be transported to a disposal or recycling facility. A small project might cost a few hundred dollars, while larger projects involving the removal of multiple layers of siding or specialized materials could reach several thousand. Obtaining multiple quotes from waste removal companies is highly recommended to ensure you are getting a competitive price. Many companies offer both dumpster rental services and full-service removal, where they handle all aspects of waste collection and disposal.
Environmentally Responsible Disposal Methods for Old Siding Materials
Many siding materials can be recycled or repurposed, reducing landfill waste and minimizing environmental impact. For example, some types of vinyl siding can be recycled through specialized programs, while wood siding may be suitable for use as firewood (after ensuring it’s free of harmful treatments) or repurposed for other construction projects. Asbestos siding, however, requires special handling and disposal due to its hazardous nature. It’s crucial to identify the type of siding being removed to determine the appropriate disposal method. Contractors experienced in siding replacement should be knowledgeable about environmentally sound disposal options and be able to provide information on local recycling programs or disposal facilities that accept construction debris. Choosing a contractor committed to sustainable practices is a valuable step towards responsible waste management.
Examples of Local Regulations Regarding Waste Disposal for Construction Projects
Local regulations regarding construction waste disposal vary widely. Many municipalities have specific ordinances concerning the permitted disposal methods, required permits, and potential fines for non-compliance. For example, some cities might mandate the separation of different waste streams (e.g., wood, metal, plastic), while others may have limits on the amount of waste that can be disposed of at a specific location. Before starting your siding replacement project, contact your local building department or waste management authority to obtain information on relevant regulations, required permits, and disposal fees. Understanding these regulations upfront will help you avoid potential delays, fines, and additional expenses associated with improper waste disposal. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties, making proactive research a cost-effective measure.
Insurance and Warranties
Protecting your investment in a new siding installation requires careful consideration of insurance and warranties. Understanding the coverage offered by both your insurance provider and the siding contractor is crucial to ensuring a smooth and worry-free project. Unexpected issues can arise, and having the appropriate protection in place can save you significant financial burdens.
Importance of Insurance Coverage During a Home Improvement Project
Comprehensive insurance coverage is vital during a home siding replacement. General liability insurance held by the contractor protects you from financial losses should accidents occur on your property during the project, such as worker injury or damage to neighboring properties. Additionally, it’s advisable to review your homeowner’s insurance policy to confirm sufficient coverage for damage to your home during the renovation, including potential damage from unforeseen weather events during the construction phase. This could cover expenses related to temporary repairs or additional costs resulting from project delays due to weather-related damage. For example, a sudden hailstorm during installation could damage both the new and existing siding, necessitating additional repair costs that your homeowner’s insurance might cover.
Types of Warranties Offered by Siding Manufacturers and Contractors
Siding manufacturers typically offer warranties on their products, covering defects in materials and workmanship for a specified period. These warranties can vary significantly in length and the types of defects covered. Some manufacturers offer limited warranties covering only manufacturing defects, while others offer more comprehensive warranties that also cover issues like fading or cracking due to normal wear and tear, although often with specific conditions and limitations. Contractors also provide warranties on their labor, typically covering issues related to their installation work for a set period, such as improper installation leading to leaks or premature failure of the siding. The length and scope of contractor warranties can vary greatly depending on the contractor’s experience and reputation.
Comparison of Warranty Options and Coverage
A manufacturer’s warranty might cover defects in the siding material for 20 years, but exclude damage caused by improper installation. Conversely, a contractor’s warranty might cover installation defects for 10 years but not the underlying material itself. Therefore, understanding the specific terms and conditions of both the manufacturer’s and contractor’s warranties is essential. A strong siding installation typically combines a robust manufacturer’s warranty with a comprehensive contractor’s warranty, providing more extensive protection against potential problems. For example, if a section of siding fails after five years due to a manufacturing defect, the manufacturer’s warranty would likely cover the replacement cost of the siding. However, if the failure is due to improper installation, the contractor’s warranty should cover the repair or replacement. Comparing warranties involves careful review of the fine print, paying close attention to exclusions and limitations, and understanding how the manufacturer’s and contractor’s warranties interact. Some contractors might offer extended warranties at an additional cost, providing even greater peace of mind.
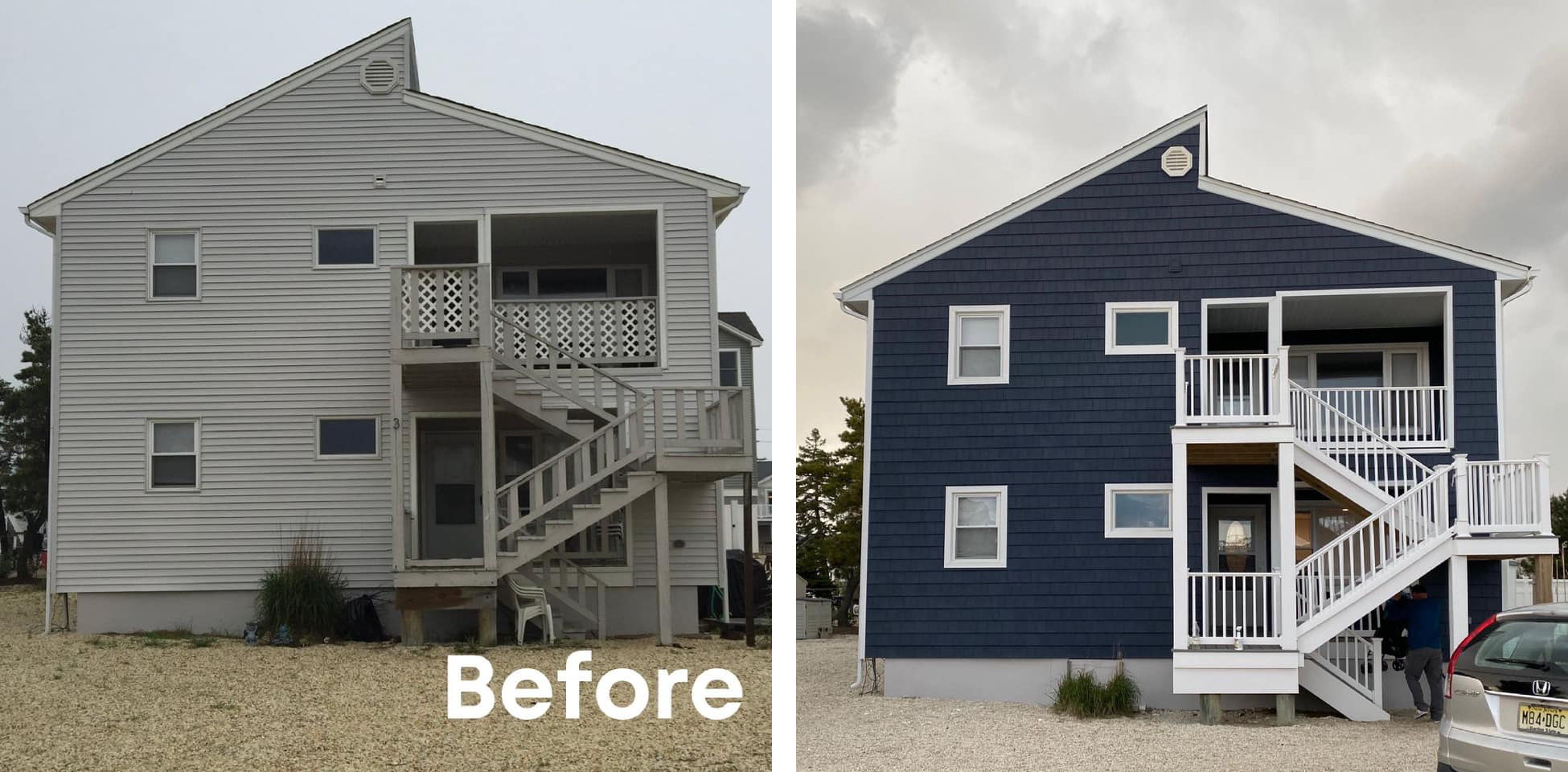
Visual Aids: Before & After Scenarios
Choosing new siding is a significant decision impacting your home’s curb appeal and value. Visualizing the transformation is crucial, and before-and-after scenarios can greatly assist in this process. Reviewing examples of different siding types on various home styles allows for a clearer understanding of the potential impact of a full home siding replacement.
Before and After Scenarios: Siding Types and Home Styles
The visual impact of a siding replacement varies considerably depending on the original siding, the chosen replacement, and the architectural style of the home. Below are a few examples illustrating these differences.
Example 1: Ranch Style Home – Vinyl to Fiber Cement
Before: Imagine a single-story ranch home with aged, faded beige vinyl siding. The siding shows signs of wear, with some discoloration and cracking. The overall appearance is somewhat drab and lacks visual interest.
After: The same ranch home now features sleek, charcoal gray fiber cement siding. The new siding provides a clean, modern look, enhancing the home’s architectural lines. The dark gray color creates a striking contrast against the lighter-colored trim and foundation, adding depth and visual appeal. The improved texture and consistent color dramatically enhance the home’s curb appeal.
Example 2: Victorian Style Home – Wood Shake to Engineered Wood
Before: Picture a Victorian-style home with weathered wood shake siding. The shakes are uneven in color and texture, showing signs of age and damage. The overall appearance is somewhat rustic, but also slightly unkempt.
After: The same Victorian home is now clad in rich, dark brown engineered wood siding. The new siding maintains the home’s historical character while providing a more polished and updated look. The consistent color and even texture enhance the intricate details of the home’s architecture, creating a more elegant and refined appearance. The improved weather resistance also suggests a longer lasting solution.
Example 3: Colonial Style Home – Aluminum to Insulated Vinyl
Before: Consider a colonial-style home with outdated aluminum siding. The aluminum siding is showing significant signs of fading and pitting, with a generally dull and lifeless appearance.
After: The same colonial home boasts crisp white insulated vinyl siding. The new siding provides a clean, classic look that complements the home’s architectural style. The bright white color creates a feeling of spaciousness and elegance. The improved insulation properties, though not directly visible, are a significant benefit alongside the improved aesthetics. The smooth, consistent surface of the vinyl enhances the overall visual appeal.
Example 4: Modern Farmhouse – Brick to Board and Batten
Before: A modern farmhouse with exposed brick showing signs of age and discoloration. The brick might be uneven in color and texture, creating a somewhat inconsistent appearance.
After: The same farmhouse is now clad in clean, white board and batten siding. The board and batten siding adds a fresh, modern farmhouse aesthetic while maintaining a rustic feel. The crisp white siding contrasts beautifully with darker accents, such as window frames and rooflines, creating a striking and visually appealing result. The vertical lines of the board and batten siding add visual interest and draw the eye upwards.
Impact on Home Value
Replacing your home’s siding is a significant investment, but it can offer a substantial return in terms of increased home value. A well-chosen and professionally installed siding system can dramatically improve your home’s curb appeal and overall condition, making it more attractive to potential buyers and increasing its market value. The extent of this increase depends on several key factors.
The potential increase in home value from a siding replacement varies depending on several factors. A high-quality, durable siding material, like fiber cement or engineered wood, will generally yield a higher return on investment than a less expensive option. Similarly, the overall condition of the home, the location, and the current market trends all play a role. A beautifully updated home in a desirable neighborhood will naturally see a greater increase in value compared to a similar upgrade in a less sought-after area.
Return on Investment Factors
Several factors influence the return on investment (ROI) for siding upgrades. These factors should be carefully considered before embarking on the project.
The choice of siding material significantly impacts the ROI. While less expensive vinyl siding might offer a quicker payback, it may not increase home value as much as higher-end materials such as fiber cement or brick. The longevity and durability of the chosen material also play a crucial role. A longer-lasting siding system will require less maintenance over time, resulting in long-term cost savings and a potentially higher ROI.
The condition of the existing siding and the overall state of the home influence the return. Replacing severely damaged or outdated siding will yield a greater increase in home value than simply replacing relatively new siding. Addressing other home improvements simultaneously, such as window replacements or landscaping, can further enhance the impact of the siding upgrade. A comprehensive approach to home improvement can result in a synergistic effect, maximizing the return on investment.
Location and market conditions play a significant role. In a competitive real estate market, a well-maintained home with attractive siding will likely command a higher price than a comparable home with outdated or damaged siding. Conversely, in a buyer’s market, the return on investment might be lower. Consulting with a real estate agent can provide valuable insights into local market trends and the potential impact of siding replacement on home value in your specific area.
For example, let’s consider two homes in the same neighborhood. Home A has outdated vinyl siding, while Home B undergoes a complete siding replacement with high-quality fiber cement. Assuming all other factors are equal, Home B is likely to sell for a significantly higher price due to the improved curb appeal and perceived higher quality. The higher cost of fiber cement siding would be offset by the increased market value. Similarly, a home in a highly desirable area with updated siding will see a larger increase in its value compared to a similar home in a less desirable area.
Appraisal Impact
A professional appraisal can provide a quantifiable assessment of the increase in home value resulting from the siding replacement. An appraiser will consider factors such as the type of siding, the quality of the installation, and the overall condition of the property. The appraisal report will provide a clear indication of the return on investment and can be used to support financing applications or insurance claims. This objective assessment provides valuable data for informed decision-making.
Creating a Comprehensive Budget Spreadsheet
A well-organized budget spreadsheet is crucial for managing the costs associated with a full home siding replacement project. This spreadsheet will allow you to track expenses, compare bids, and ensure you stay within your financial limits. A detailed and organized approach will minimize surprises and help you make informed decisions throughout the process.
Spreadsheet Design and Categories
The following table outlines a suggested structure for your siding replacement budget spreadsheet. Each category should have its own column, allowing for easy tracking and comparison of costs from different contractors or material suppliers. Remember to update the spreadsheet regularly as the project progresses.
| Category | Description | Estimated Cost | Actual Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material Costs | Siding, trim, flashing, fasteners, etc. | Include detailed breakdown of materials and quantities. | ||
| Labor Costs | Contractor fees, labor for demolition, installation, etc. | Specify hourly rates or lump sum payments. | ||
| Permits and Inspections | Building permits, inspection fees | Include all relevant permit applications and inspection costs. | ||
| Contractor Selection | Bid comparisons, contractor fees, contract review | List multiple bids and the reasons for selection. | ||
| Hidden Costs | Unexpected repairs, material adjustments, etc. | Allocate a contingency for unforeseen expenses. | ||
| Contingency | Buffer for unexpected costs (typically 10-20% of total estimated cost) | This is crucial for managing risk. | ||
| Financing Options | Loan interest, down payment, monthly payments | Specify loan terms and repayment schedule. | ||
| Project Timeline and Scheduling | Project start and completion dates, milestones | Track progress against planned timeline. | ||
| Waste Removal and Disposal | Dumpster rental, debris removal fees | Include costs for proper waste disposal. | ||
| Insurance and Warranties | Contractor’s insurance, material warranties | Verify insurance coverage and warranty details. | ||
| Total Estimated Cost | Sum of all estimated costs | This is your initial project budget. | ||
| Total Actual Cost | Sum of all actual costs | This will be updated as the project progresses. |
Using Formulas for Accurate Calculations
The spreadsheet should utilize formulas to automatically calculate totals. For example, the “Total Estimated Cost” can be calculated by summing all the estimated costs in the “Estimated Cost” column. Similarly, the “Total Actual Cost” should be calculated automatically as the project progresses. This will ensure accuracy and reduce the risk of manual calculation errors. For instance, a simple formula for the total estimated cost would be: =SUM(B2:B11) (assuming estimated costs are in column B, rows 2 through 11).
Visual Aids for Tracking Progress
Consider adding a visual representation of the budget, such as a bar chart or pie chart, to track progress and identify areas where costs are exceeding or falling short of the estimates. This visual aid can provide a clear and concise overview of the budget’s status at a glance. For example, a bar chart could show the allocated budget for each category versus the actual spent amount. A pie chart could illustrate the proportion of the total budget allocated to each cost category.
Closure
Replacing your home’s siding is a significant investment, but with careful planning and budgeting, it can be a rewarding experience. By understanding the various cost components—materials, labor, permits, and potential unforeseen expenses—and exploring available financing options, you can create a realistic budget that aligns with your financial capabilities. Remember to factor in contingency funds for unexpected issues and choose reputable contractors with clear contracts and warranties. The result will be a beautiful, durable, and valuable upgrade to your home, enhancing its curb appeal and potentially increasing its market value.