How to Get Accurate Siding Replacement Estimates is crucial for a successful home improvement project. Replacing your siding is a significant investment, and understanding the process of obtaining precise estimates is paramount to avoiding costly surprises and ensuring a smooth renovation. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of siding replacement, from understanding the scope of work to negotiating fair prices and securing appropriate warranties.
This comprehensive guide breaks down the process into manageable steps, covering everything from accurately measuring your home’s exterior to selecting reputable contractors and understanding the intricacies of different siding materials. We’ll explore how to decipher detailed estimates, identify potential hidden costs, and navigate the complexities of permits, inspections, and financing options. By the end, you’ll be confident in your ability to obtain accurate estimates and make informed decisions for your siding replacement project.
Understanding the Scope of Work
Accurately estimating the cost of siding replacement requires a thorough understanding of the project’s scope. Several factors contribute to the final price, and neglecting any of them can lead to significant discrepancies between the estimate and the actual cost. A detailed assessment of these factors is crucial for both homeowners and contractors to ensure a fair and accurate price.
Several key factors influence the cost of siding replacement. These factors interact in complex ways, so a comprehensive evaluation is necessary for a precise estimate.
Factors Influencing Siding Replacement Costs
The cost of siding replacement is determined by a combination of material costs, labor costs, and the complexity of the project. Material costs vary significantly depending on the type of siding chosen (e.g., vinyl, wood, fiber cement), its quality, and its aesthetic features. Labor costs are influenced by the size of the house, the condition of the existing siding (requiring more or less demolition and preparation), the accessibility of the work area (scaffolding needs?), and the contractor’s experience and overhead. Additional factors include permits, waste disposal, and any unforeseen repairs discovered during the project. For example, a large two-story home with intricate architectural details will naturally require more labor and potentially more expensive materials than a smaller, simpler ranch-style house. A project requiring significant removal of rotted wood will also add to the overall cost.
Measuring the Area Needing Siding Replacement
Accurate measurement of the area requiring siding replacement is paramount for obtaining an accurate estimate. This involves more than simply calculating the square footage of the house’s exterior walls. Detailed measurements should account for windows, doors, vents, and other features that will not require new siding. The process typically involves using a measuring tape to determine the linear dimensions of each wall section, then subtracting the areas of openings. Professional contractors often use specialized software to create a detailed plan of the house, facilitating precise calculations and material ordering. For instance, measuring a 20ft x 30ft wall section with a single 3ft x 7ft window would involve calculating the total wall area (600 sq ft) and subtracting the window area (21 sq ft) resulting in 579 sq ft of siding needed for that particular section. This process is repeated for every section of the house requiring new siding.
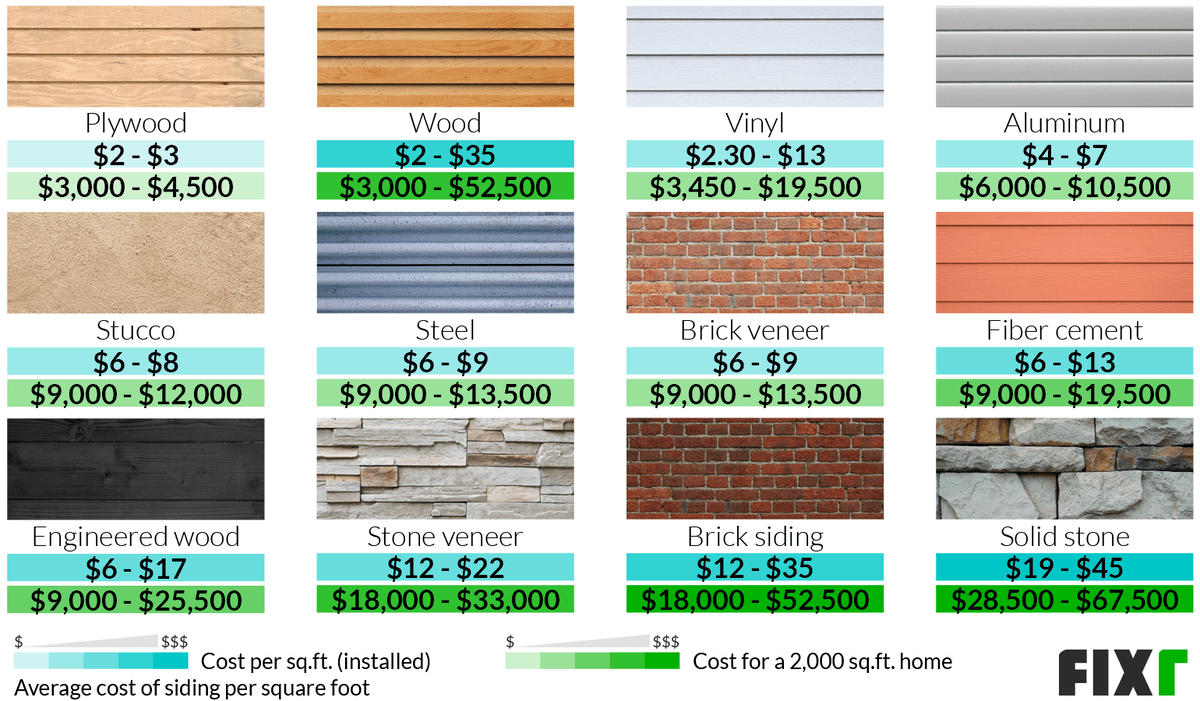
Siding Material Types and Their Cost Impact
Different siding materials significantly impact the overall project cost. Vinyl siding is generally the most affordable option, offering a balance of durability and cost-effectiveness. However, it might not be as aesthetically pleasing or long-lasting as other options. Wood siding, while offering a classic look, is more expensive and requires more maintenance. Fiber cement siding provides excellent durability and fire resistance but is typically more costly than vinyl. Metal siding, such as aluminum or steel, offers exceptional durability and longevity, but often comes with a higher price tag. The choice of siding material directly affects not only the material cost but also the labor cost, as different materials require different installation techniques and expertise. For example, installing intricate wood siding requires specialized skills and thus a higher labor cost compared to installing vinyl siding.
Finding Reputable Contractors
Choosing the right contractor is crucial for a successful siding replacement project. A reputable contractor possesses the necessary experience, licensing, and insurance to ensure quality workmanship and protect you from potential liabilities. Thorough vetting is essential to avoid costly mistakes and project delays.
Selecting a contractor involves careful consideration of their experience, licensing, insurance, and bidding process. This section provides guidance on how to effectively assess these critical factors.
Contractor Experience and Reliability Assessment
To gauge a contractor’s experience and reliability, several key questions should be addressed. Gathering this information will help you make an informed decision. Consider asking about the number of years they’ve been in business, their specific experience with siding replacement (including the types of siding they’ve worked with), and the size and scope of past projects similar to yours. Inquiring about their process for managing projects, including timelines and communication, will provide further insight into their professionalism. Furthermore, requesting references from previous clients allows you to independently verify their work quality and overall customer satisfaction. Finally, reviewing online reviews and testimonials can provide valuable additional insights into their reputation.
Verification of Contractor Licenses and Insurance
Verifying a contractor’s license and insurance is a critical step in protecting yourself from potential problems. Contact your state’s licensing board to confirm the contractor’s license is valid, current, and in good standing. This verification process helps ensure the contractor meets the minimum standards of competence and professionalism required by your state. Similarly, request proof of general liability and workers’ compensation insurance. General liability insurance protects you from financial losses if an accident occurs on your property during the project. Workers’ compensation insurance covers medical expenses and lost wages for employees injured on the job, protecting you from potential liability for their injuries. Failure to verify these crucial elements could leave you exposed to significant financial risks.
Comparison of Contractor Bidding Processes
Contractors utilize different bidding processes, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some contractors provide fixed-price bids, offering a total cost for the entire project upfront. This approach provides clarity and predictability regarding the final cost, but it may not account for unforeseen issues that could arise during the project. Other contractors use cost-plus bids, where the final cost is determined by the actual materials and labor used. This method offers flexibility to address unexpected issues, but it can lead to cost overruns if not carefully managed. Finally, some contractors provide a range of estimated costs, acknowledging potential variations in the final price based on factors discovered during the project. Understanding these differences is key to selecting a bidding process that aligns with your project’s needs and risk tolerance. For example, a complex project with potential for unforeseen issues might benefit from a cost-plus bid, while a straightforward project might be better suited to a fixed-price bid.
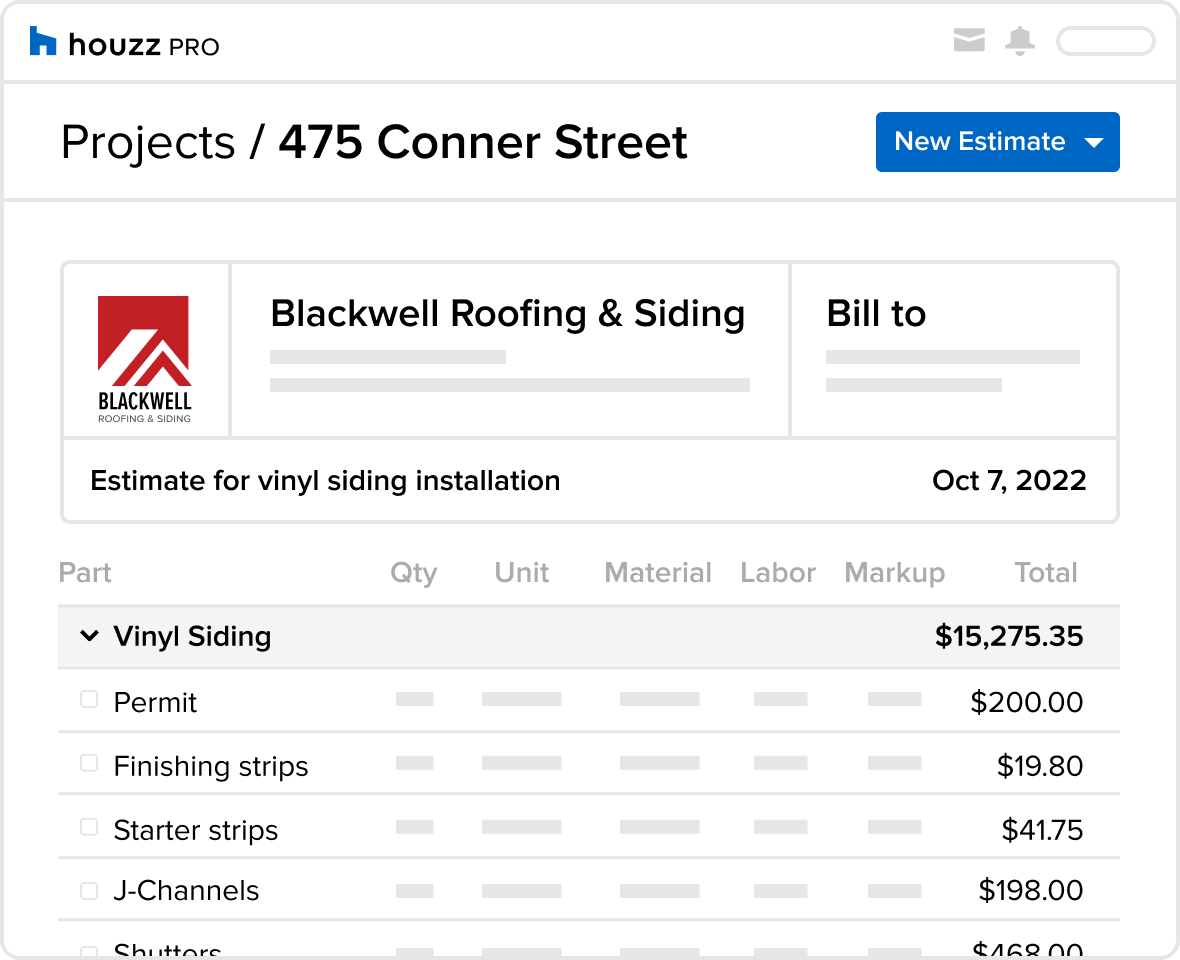
Detailed Breakdown of Estimates
Receiving a detailed estimate is crucial for a successful siding replacement project. A comprehensive breakdown allows you to compare quotes effectively, understand the true cost, and avoid unexpected expenses. A transparent estimate builds trust with the contractor and ensures you’re both on the same page regarding the project’s scope and financial implications.
A well-structured estimate should clearly outline all costs associated with the project. This includes labor, materials, permits, and any other potential expenses. Failing to receive a detailed breakdown can lead to disagreements and cost overruns later in the process.
Sample Estimate Template
A clear and organized estimate significantly simplifies the comparison process. The following table illustrates a sample estimate template that contractors should use:
| Item | Labor Cost | Materials Cost | Permits & Fees |
|---|---|---|---|
| Siding Removal & Disposal | $XXX | $XXX | $0 |
| Sheathing Repair (if needed) | $XXX | $XXX | $0 |
| New Siding Installation | $XXX | $XXX | $0 |
| Flashing & Caulking | $XXX | $XXX | $0 |
| Permit Acquisition | $0 | $0 | $XXX |
| Clean Up | $XXX | $0 | $0 |
| Total | $XXX | $XXX | $XXX |
Note: Replace the “$XXX” placeholders with the actual costs provided by the contractor. Remember that prices will vary depending on factors such as location, materials chosen, and the size of the project.
Detailed Materials List
The inclusion of a detailed materials list is paramount. This list should specify the type, quantity, and brand of each material to be used. For example, instead of simply stating “siding,” the list should detail the type of siding (e.g., vinyl, fiber cement, wood), its color, manufacturer, and the square footage needed. This level of detail allows for accurate cost comparisons and ensures that you understand exactly what materials will be used in your project. Discrepancies between the quoted materials and those actually used should be immediately addressed.
Potential Hidden Costs and Their Identification
Unforeseen costs can significantly impact the final project price. Common hidden costs include unexpected repairs to underlying sheathing, additional labor required due to unforeseen complications (e.g., rotted wood), changes in material pricing, and disposal fees. To identify potential hidden costs, carefully review the estimate for any vague or unspecified items. Ask the contractor clarifying questions about any ambiguous entries and request a detailed breakdown of any additional charges that may arise. It is prudent to obtain multiple estimates to compare pricing and identify any potential discrepancies. For example, one contractor might include sheathing repair in their base price, while another might list it as an add-on, potentially leading to a higher final cost.
Material Costs and Pricing
Understanding material costs is crucial for accurate siding replacement estimates. The type of siding you choose significantly impacts both the initial expense and the long-term cost of ownership. Different materials offer varying levels of durability, maintenance requirements, and aesthetic appeal, all of which influence the overall price.
Siding Material Price Comparison
Vinyl, wood, and fiber cement are common siding choices, each with its own price range. Vinyl siding is generally the most affordable option, offering a wide range of colors and styles at a lower cost per square foot compared to wood or fiber cement. Wood siding, particularly premium varieties like cedar or redwood, commands a significantly higher price due to its natural beauty and inherent characteristics. Fiber cement siding falls somewhere in between, providing a durable, low-maintenance alternative at a cost often exceeding vinyl but generally less than high-end wood. Price fluctuations are common depending on the specific manufacturer, finish, and regional availability. For example, a basic vinyl siding might cost between $3 and $8 per square foot installed, while high-end wood siding could range from $15 to $30 or more. Fiber cement typically falls within $8 to $15 per square foot installed. These figures are estimates and can vary widely based on several factors.
Material Quality and Longevity
The quality of siding materials directly impacts both the upfront cost and the long-term expenses associated with maintenance and replacement. Higher-quality materials, while more expensive initially, often offer superior durability, resistance to weather damage, and a longer lifespan, ultimately reducing the total cost of ownership over time. For instance, a thicker, more robust vinyl siding with a better warranty will cost more upfront but is less likely to require repairs or replacement within a shorter timeframe compared to a thinner, less expensive option. Similarly, higher-grade wood siding, treated for rot and insect resistance, will be more expensive but require less maintenance and last longer than untreated wood. Fiber cement siding, known for its fire resistance and durability, also exhibits a longer lifespan, though higher-quality options within this category will typically come with a higher price tag.
Obtaining Multiple Material Quotes
Securing multiple quotes for siding materials from different suppliers is essential for ensuring you receive competitive pricing. Contact at least three to five different suppliers, providing them with detailed specifications of your siding needs, including the type of material, quantity, color, and any special features. Compare not only the price per unit but also the total cost, including delivery fees and any applicable taxes. Be sure to clarify the warranty offered on the materials and inquire about potential discounts or bulk purchase options. This comparative approach will enable you to make an informed decision and potentially save a significant amount of money on your siding project. Remember to verify the supplier’s reputation and reliability before committing to a purchase.
Labor Costs and Timelines
Understanding labor costs and project timelines is crucial for accurate siding replacement budgeting. These factors, often intertwined, significantly impact the overall cost and can vary considerably depending on several key variables. Accurate estimation requires a careful consideration of these variables to avoid unexpected expenses and delays.
Labor costs for siding replacement are influenced by several factors. The experience level of the crew directly affects the speed and efficiency of the work, leading to variations in overall labor costs. More experienced crews, while commanding higher hourly rates, often complete the job faster, potentially offsetting the higher cost per hour with reduced overall labor time. Geographical location also plays a significant role; labor rates in high-cost-of-living areas tend to be higher than in more affordable regions. Finally, project complexity, including the size of the house, the type of siding being installed, and the presence of intricate architectural details or difficult-to-access areas, all contribute to increased labor hours and therefore higher costs.
Factors Affecting Labor Costs
Several factors influence the final labor costs associated with a siding replacement project. These include the experience and skill level of the workers, the prevailing wage rates in the specific geographic location, and the complexity of the project itself. For instance, a larger, more complex project with intricate detailing will naturally require more labor hours than a smaller, simpler project. Similarly, a crew with extensive experience in siding installation will likely complete the work more efficiently than a less experienced team, potentially leading to lower overall labor costs despite higher hourly rates. The type of siding material also influences labor costs; some materials are more challenging to install than others, impacting the time required and, consequently, the labor expenses.
Realistic Timelines for Siding Replacement Projects
The timeline for a siding replacement project varies greatly depending on the size of the house, the complexity of the design, and weather conditions. A small house with simple siding might take a few days to a week, while a larger, more complex project could take several weeks or even months. For example, a 1,500 square foot ranch-style home with standard vinyl siding might be completed within 7-10 business days by an experienced crew. However, a 3,000 square foot Victorian home with intricate detailing and multiple materials might take 4-6 weeks or longer. Unforeseen circumstances, such as inclement weather, material delays, or unexpected structural issues, can further extend the project timeline. It’s crucial to discuss realistic timelines with contractors and factor in potential delays during the planning phase.
Negotiating Labor Costs
Negotiating labor costs requires a balance between securing a fair price and ensuring quality workmanship. Before negotiating, obtain multiple detailed estimates from reputable contractors. Compare not only the total cost but also the breakdown of labor and materials. Ask for clarification on any unclear items in the estimate. If a contractor’s labor cost seems significantly higher or lower than others, inquire about the reasoning behind the difference. Focus on the value proposition—experience, warranty, materials used—rather than solely on the price. Remember that a slightly higher upfront cost might be justified by superior quality and a shorter project timeline, potentially saving you time and stress in the long run. Always ensure that the agreed-upon labor costs are clearly outlined in a written contract before work begins.
Permits and Inspections
Obtaining the necessary permits and undergoing inspections are crucial steps in a successful siding replacement project. These processes ensure your project complies with local building codes, protects your investment, and helps guarantee the quality of the workmanship. Ignoring these steps can lead to fines, legal issues, and potential safety hazards.
Permitting Process for Siding Replacement
Securing the necessary permits typically involves submitting an application to your local building department. This application will require detailed information about the project, including the type of siding being used, the scope of work, and often, detailed drawings or plans. The review process can vary depending on your location and the complexity of the project; expect delays of a few days to several weeks. You’ll likely need to pay a fee, the amount of which varies by jurisdiction and project size. For example, a small residential siding replacement might cost between $100 and $500, while larger commercial projects could cost significantly more. After review and approval, the permit will be issued, allowing you to legally commence work. Failure to obtain a permit before starting work can result in stop-work orders, fines, and potential legal action.
Importance of Inspections
Inspections are conducted by building officials at various stages of the project to verify compliance with building codes and ensure the work meets minimum quality standards. These inspections typically occur after the preparation of the existing siding, during the installation of new siding, and after completion. Inspectors will assess aspects such as proper installation techniques, adherence to code requirements for flashing and water management, and overall quality of materials. A failed inspection may require corrective work before the project can be completed and signed off. This ensures the long-term durability and safety of your siding and protects your home from potential damage. A positive inspection, on the other hand, offers peace of mind and protects your investment.
Costs Associated with Permits and Inspections
The costs associated with permits and inspections are typically separate from the contractor’s estimate. Permit fees vary significantly by location and project scope. Inspection fees are usually charged per inspection, with the number of inspections depending on the project’s complexity. For instance, a small residential project might involve two or three inspections, each costing between $50 and $150. Therefore, budgeting for these additional costs is essential for accurate project cost planning. It is always advisable to inquire about permit and inspection fees directly with your local building department to get the most accurate estimate for your specific project.
Warranty and Guarantees
Securing a comprehensive warranty is crucial when investing in siding replacement. Understanding the types of warranties offered, their terms, and limitations will protect your investment and ensure you receive the promised quality and service. This section will clarify the different warranties involved and highlight their importance in your decision-making process.
Siding warranties typically come from two sources: the manufacturer and the contractor. Manufacturer warranties cover defects in the siding material itself, such as flaws in manufacturing or material failure due to inherent weaknesses. Contractor warranties, on the other hand, cover the workmanship of the installation. These warranties often overlap but address different aspects of the project’s success. It’s vital to carefully review both to understand the complete coverage.
Manufacturer Warranties
Manufacturer warranties vary considerably depending on the siding material (vinyl, fiber cement, wood, etc.) and the specific product line. Some offer limited warranties covering defects for a specific period, typically ranging from 10 to 50 years, while others offer more comprehensive warranties that include labor and material costs for repairs. For example, a high-end vinyl siding manufacturer might offer a 50-year warranty against fading, cracking, and peeling, while a less expensive option may only provide a 20-year warranty against manufacturing defects. Always obtain a copy of the manufacturer’s warranty documentation before making a purchase. Pay close attention to what is and is not covered, including exclusions related to improper installation or damage from extreme weather events.
Contractor Warranties
Contractor warranties primarily cover the quality of the installation. A typical contractor warranty might cover issues such as leaks, improper flashing, or faulty installation leading to siding damage within a specific timeframe, usually 1-2 years. Some contractors offer extended warranties for an additional fee, providing longer-term protection against workmanship issues. It’s important to note that contractor warranties often require adherence to specific maintenance guidelines. Failure to maintain the siding properly might void the warranty. For instance, a contractor might require annual cleaning and inspection of the siding to ensure the warranty remains valid.
Warranty Limitations
Understanding the limitations of both manufacturer and contractor warranties is paramount. Warranties rarely cover damage caused by acts of God (e.g., hurricanes, tornadoes), vandalism, or improper maintenance. They may also exclude damage resulting from modifications or alterations to the siding after installation. Some warranties contain stipulations about the use of specific cleaning products or repair methods. For example, using abrasive cleaners could void a warranty. Before signing any contract, carefully read the fine print to understand the scope of coverage and any exclusions that may apply. Clarify any ambiguities with the contractor or manufacturer to avoid misunderstandings later. A thorough understanding of warranty limitations ensures realistic expectations and prevents potential disputes down the line.
Payment Schedules and Financing Options
Securing financing and establishing a clear payment schedule are crucial aspects of your siding replacement project. Understanding the different options available and their implications will help you make informed decisions and ensure a smooth process. This section outlines typical payment structures and financing choices to consider.
Payment schedules generally align with project milestones. A common approach involves several installments tied to specific stages of completion. This protects both the homeowner and the contractor, ensuring fair compensation for work performed.
Sample Payment Schedule
A typical payment schedule might look like this:
| Milestone | Payment Percentage |
|---|---|
| Contract signing and material ordering | 10% |
| Completion of demolition and preparation | 20% |
| Completion of installation (50%) | 30% |
| Final inspection and completion | 40% |
Note: These percentages are examples, and the actual schedule will depend on the specifics of your project and agreement with the contractor. Always review the payment schedule carefully before signing the contract.
Financing Options for Siding Replacement
Several financing options exist to help manage the cost of siding replacement. These can significantly impact your overall budget and repayment plan.
Homeowners can explore various financing routes, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Home Equity Loan or Line of Credit (HELOC)
Home equity loans and HELOCs utilize the equity in your home as collateral. They typically offer lower interest rates than personal loans but carry the risk of foreclosure if payments are not met. The approval process involves a credit check and appraisal of your property. A significant advantage is the potential for tax deductibility of the interest.
Personal Loan
Personal loans are unsecured loans, meaning they don’t require collateral. They offer flexibility in terms of repayment schedules but often come with higher interest rates compared to home equity loans. Approval depends on your credit score and income.
Contractor Financing
Some contractors offer financing options directly to their clients. This can streamline the process, but it’s crucial to understand the terms and interest rates carefully. These plans might have limitations on the amount financed or specific repayment periods.
Credit Cards
Using credit cards can be a convenient short-term solution, but high interest rates can make it a costly option if not paid off quickly. Careful budgeting and prompt repayment are crucial to avoid accumulating significant debt.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Payment Methods
The best payment method depends on your individual financial situation and the terms offered by your contractor. Carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages before making a decision.
| Payment Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | Often results in a lower overall cost due to the absence of interest. | Requires a significant upfront capital investment. |
| Home Equity Loan/HELOC | Potentially lower interest rates, tax deductibility. | Uses home equity as collateral, risks foreclosure. |
| Personal Loan | Flexible repayment schedules, no collateral needed (usually). | Typically higher interest rates compared to home equity loans. |
| Contractor Financing | Streamlined process. | Potentially limited options, interest rates may vary. |
| Credit Cards | Convenience. | High interest rates if not paid promptly. |
Addressing Unexpected Issues
Siding replacement projects, while meticulously planned, can sometimes encounter unforeseen complications. Understanding these possibilities and how they’re handled is crucial for a smooth and successful renovation. Proper communication between the contractor and homeowner is key to navigating these challenges effectively.
Unexpected issues during a siding replacement project can significantly impact both the timeline and the final cost. Therefore, it’s vital to have a plan in place to address these contingencies. This involves proactive communication from the contractor, transparency about additional costs, and a clearly defined process for handling changes to the original scope of work.
Examples of Unexpected Issues
During a siding replacement, various unforeseen problems can arise. These often involve underlying structural issues or deterioration not visible during the initial inspection. For instance, extensive rotted wood beneath the existing siding might necessitate more extensive repairs than initially anticipated. Similarly, discovering damaged sheathing or structural framing requires addressing these issues before new siding can be installed. Other unexpected issues might include discovering lead paint, requiring specialized and more costly abatement procedures, or encountering unexpected obstacles such as underground utilities or difficult-to-access areas.
Contractor Handling of Unforeseen Problems
When unexpected issues arise, a reputable contractor will promptly inform the homeowner. This communication should include a clear explanation of the problem, its potential impact on the project timeline and budget, and proposed solutions. They should provide photographic evidence of the issue and discuss different options for repair, outlining the associated costs for each. The contractor should obtain the homeowner’s approval before proceeding with any additional work. Detailed documentation of these changes, including photos and written agreements, is crucial for maintaining transparency and avoiding future disputes.
Accounting for Potential Unexpected Expenses in the Estimate
While it’s impossible to predict every possible issue, a comprehensive estimate should include a contingency clause. This clause acknowledges the possibility of unforeseen problems and allocates a percentage (typically 5-10%) of the total estimated cost to cover unexpected expenses. This contingency fund allows for the resolution of minor problems without requiring significant budget adjustments or project delays. A detailed breakdown of the contingency allocation should be provided to the homeowner for transparency. For example, an estimate of $10,000 might include a $500-$1000 contingency to address minor unforeseen issues such as localized wood rot or minor adjustments to flashing. Larger, more significant unforeseen problems will require separate change orders.
Final Thoughts
Securing accurate siding replacement estimates requires diligent research, careful planning, and effective communication with contractors. By following the steps outlined in this guide—from understanding the scope of work and finding reputable contractors to analyzing detailed estimates and addressing potential unexpected issues—you can confidently navigate the process and ensure a successful and cost-effective siding replacement project. Remember, a well-informed homeowner is best positioned to achieve the desired outcome within budget and timeline expectations. Take your time, ask questions, and choose wisely.